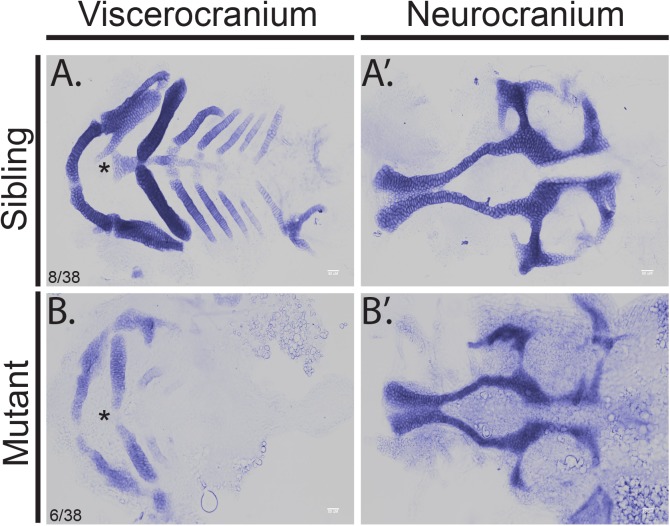
Fig 1. Mutation of hmgcs1 causes craniofacial abnormalities.
Alcian staining was performed to visualize the developing cartilage in hmgcs1 wildtype or heterozygous (Sibling) or homozygous hmgcs1 mutant larvae (Mutant). Embryos were stained at 4 days post fertilization and manual dissection of the viscerocranium and neurocranium was performed. Viscerocranium is depicted in (A) and (B) and neurocranium is depicted in (A’) and (B’). Asterisk denotes basihyal. n = 38 including 8 wildtype embryos, 6 homozygous mutants, and 24 heterozygous mutants. No significant defects were present in heterozygous carriers (S1 Fig).