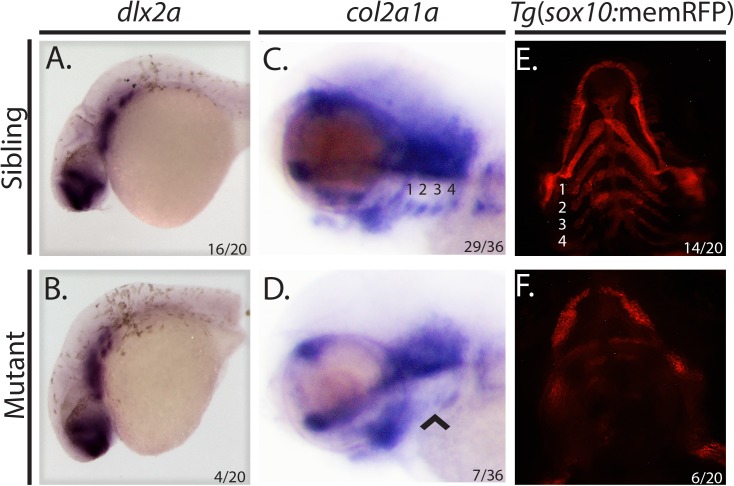
Fig 3. hmgcs1 modulates cranial neural crest cell differentiation.
(A&B) Whole mount in situ hybridization (ISH) was performed at 1 day post fertilization (dpf) between Prim-5 and Prim- 15 on wildtype/heterozyous hmgcs1 siblings (Sibling) or hmgcs1 homozygous mutant larvae (Mutant) using a riboprobe specific to dlx2a. n = 20 including 16/20 wildtype and heterozygous siblings and 4/20 homozygous mutants. Panel A depicts a wildtype sibling and no significant difference between wildtype embryos was detected. (C&D) ISH was performed at 3 dpf (protruding mouth stage) on hmgcs1 siblings (wildtype and heterozygous individuals) or hmgcs1 homozygous mutant larvae with a riboprobe specifically detecting col2a1a expression. Numbers denote the pharyngeal arch patterns present a 3dpf. Arrowhead denotes a loss of defined expression of col2a1a in hmgcs1 mutant larvae. n = 36 including 29 wildtype and heterozygous individuals with 7 homozygous mutants. Panel C depicts a wildtype sibling with no significant differences observed between wildtype and heterozygous carriers. (E&F) Tg(sox10:memRFP) hmgcs1 siblings or homozygous hmgcs1 mutant larvae were imaged for RFP expression at 3dpf at the protruding mouth stage. Numbers indicate structures that will give rise to the putative ceratobranchial cartilages. n = 20 including 14/20 wildtype and heterozygous siblings and 6/20 homozygous mutants. Panel E depicts a wildtype sibling with no significant differences observed in heterozygous carriers.