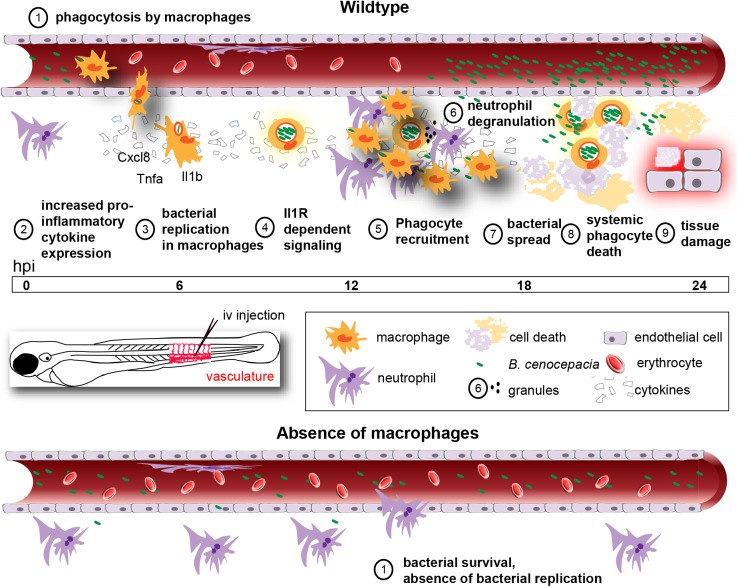
Fig 9. Schematic showing the role of macrophages during acute infection by B. cenocepacia K56-2 in zebrafish embryos.
Macrophages are the major phagocytosing cells of iv injected bacteria (1) for which they provide a critical replication niche (3). In their absence, K56-2 does not replicate (bottom panel, 1). Intracellular bacteria induce a rapid and robust increase in pro-inflammatory cytokine expression (2). Il1 signalling contributes to fatal pro-inflammatory responses (4), characterized by massive neutrophil and macrophage infiltration (5) neutrophil degranulation (6), bacterial dissemination from infected cells (7), systemic phagocyte death (8), and tissue damage (9).