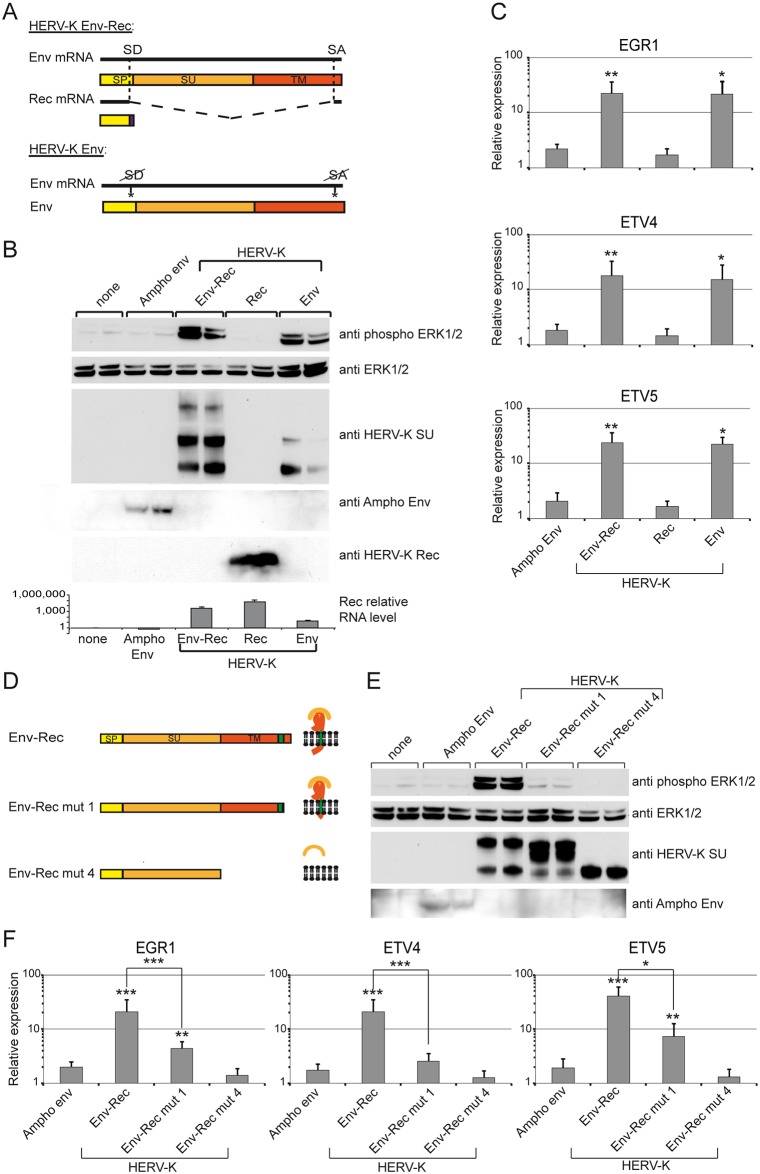
Fig 6. Mapping of the domains involved in HERV-K Env-Rec activation of the ERK1/2 pathway and induction of the transcription factors.
(A) The HERV-K Env-Rec plasmid expresses two distinct proteins via alternative splicing: the full-length RNA encodes Env, a glycoprotein that is cleaved into two subunits during synthesis (surface subunit, SU, and transmembrane subunit, TM), while internal splicing sites (SD for splice donor and SA for splice acceptor) lead to the production of the Rec accessory protein. Introducing silent mutations in the splice sites generated an expression vector that expresses Env alone. (B) The different constructs were assayed for their capacity to activate the MAPK ERK1/2 as described in Fig 3B. The expression levels of Ampho Env, HERV-K Env and HERV-K Rec were also checked by Western blot. In the case of Rec, we also performed qRT-PCR reactions on RNA samples to detect specifically the spliced Rec transcripts. (C) Transcription factor expression following transfection of the constructs above was measured as described in Fig 2C. Error bars represent the standard deviation of five independent experiments. (D) Truncation mutants of HERV-K Env were generated to identify the region required for activation of the ERK1/2 pathway. The expected protein structure of each mutant is shown on the right. All modifications were designed to change Env without altering the Rec ORF and keeping the global structure of the Env-Rec RNA. The different domains of each construct are indicated: SP (signal peptide, yellow), SU (orange), TM (red). Env-Rec mut1 corresponds to a C-terminal truncated version of the complete envelope protein. Env-Rec mut4 is the soluble surface subunit. Expression of Ampho Env and the different HERV-K Env-Rec mutants was measured together with their ability to induce phosphorylation of ERK1/2 by Western Blot (E) and expression of the transcription factors was measured by qRT-PCR (F). Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean of eight independent experiments.