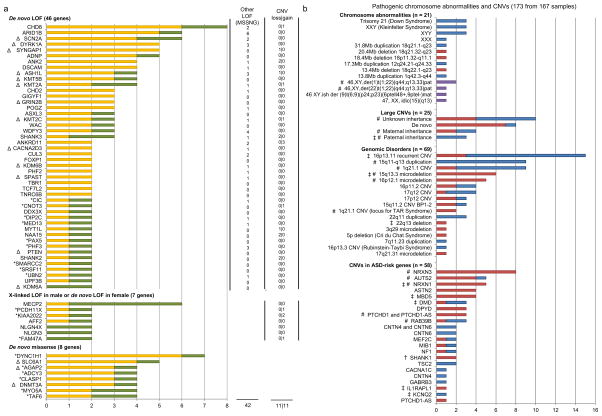
Figure 3. ASD-susceptibility genes/loci.
(a) ASD-risk genes with higher than expected mutation rate from MSSNG integrated with other large-scale high-throughput sequencing projects. ASD-risk genes are ranked in descending order of the number of mutations found for each gene. Other LOF mutations, including inherited LOF mutations and LOF mutations with unknown inheritance (where parents are unavailable for testing), and CNVs found in the MSSNG cohort are indicated (except for genes found by higher than expected de novo missense mutation rate). MSSNG data are in green and published data are in yellow. Novel putative ASD-risk genes identified in this study carry an asterisk. Δ indicate genes with druggable protein domains identified (Supplementary Table 6). (b) Pathogenic chromosomal abnormalities and CNVs identified falling into one of four categories: Chromosomal abnormalities; DECIPHER loci and other genomic disorders associated with ASD; large rare CNVs between 3–10Mb and CNVs disrupting ASD candidate genes not described above in Figure 3a. Deletions are in red, duplications are in blue and complex variants are in purple. # indicate CNVs shared between affected siblings; ‡ indicates a CNV carried by an individual with a second pathogenic CNV; † indicates a CNV shared between individuals within an extended pedigree. Details can be found in Supplementary Table 8. Examples of CNVs affecting the NRXN1 and CHD8 genes, and the PTCHD1-AS non-coding gene identified from the WGS are shown in Figure 4.