Figure 5.
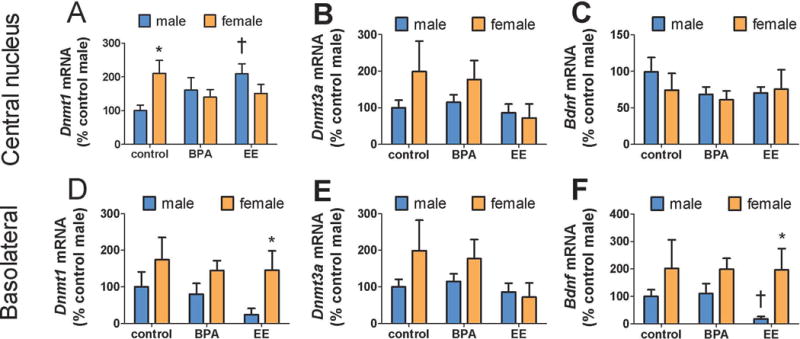
Effects of sex, BPA, and EE on gene expression in the CeA and BLA. Control females (n=11) had higher Dnmt1 expression in CeA than control males (n=11, A), but this differences was absent in BPA (females, n = 10, males, n = 9) and EE treated mice. EE diet increased Dnmt1 expression in males. In the BLA, females treated with EE (n = 9) had higher Dnmt1 expression than EE treated males (n= 7, D). No differences in Dnmt3a were observed in CeA (B) or BLA (E). The EE diet reduced male Bdnf expression in the BLA (F) but not CeA (C). * p < 0.05 effect of sex within diet, † p < 0.05 effect of diet within sex. (BPA = bisphenol A, EE = ethinyl estradiol, CeA = central amygdala, BLA = basolateral amygdala, Dnmt1 = DNA methyltransferase 1, Bdnf = brain-derived neurotrophic growth factor)
