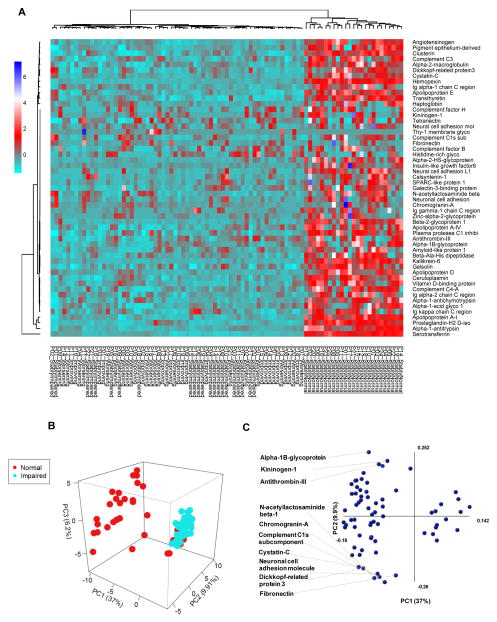
Figure 1. Relative baseline CSF protein expression in HIV-infected subjects with normal or impaired cognitive function.
Heat map and hierarchical clustering analysis showing relative baseline CSF proteomic profiles in subjects with normal cognition, stably impaired, worsening, or improving cognition. There is a general decrease in CSF proteins in subjects with impaired cognition compared to those with normal cognition. Protein identifications are on the right and patient group IDs are listed at the bottom of the figure. Heatmaps were generated using proteins common to subjects with normal and impaired cognition. Figure legend shows relationship of color to fold change in zeta score. B) Principal Components Analysis (PCA) of individual protein identifications showing separation between HIV-infected subjects with normal compared to impaired cognitive function. C) Protein components that contributed to PCA modeling are depicted in PCA1 and PCA2 axis. The top 10 proteins that contributed to the separation in PC1 are identified, and the axes show to what extent the proteins contribute to the first two principle components in the model.