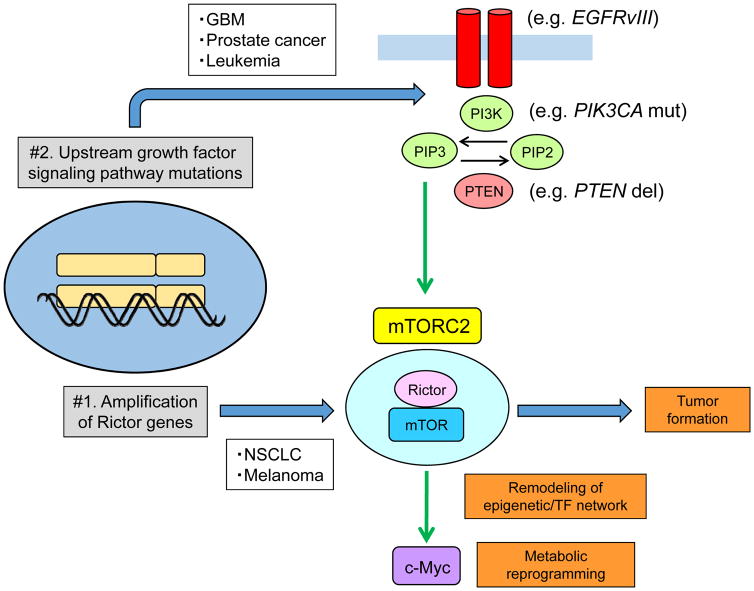
Figure 1.
mTORC2 signaling is elevated in many cancers via two distinct mechanisms.
In non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma, Rictor amplification drives mTORC2 signaling while mTORC2 signaling is hyper-activated by upstream growth factor signaling pathway mutations in prostate cancer, leukemia and GBM. Hyper-activated mTORC2 can drive tumor formation, remodel an epigenome and transcription factor network, and facilitate metabolic reprogramming through an oncogenic transcription factor c-Myc. del, deletion; EGFRvIII, epidermal growth factor receptor variant III; GBM, glioblastoma multiforme; mut, mutation; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIK3CA, phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; TF, transcriptional factor.