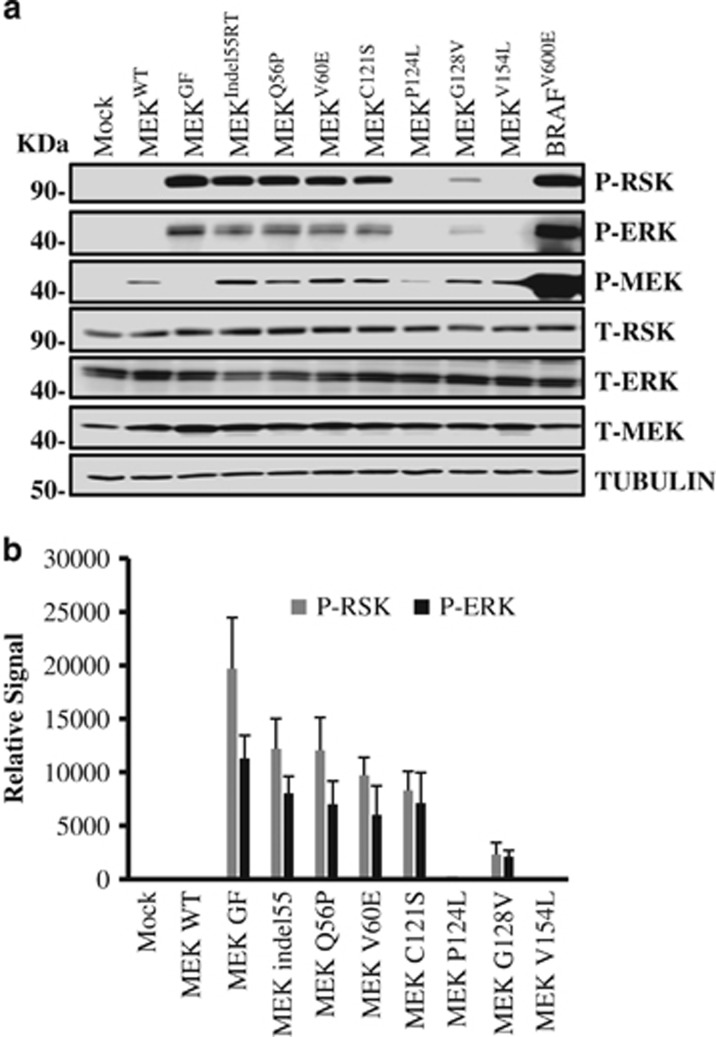
Figure 2.
Comparative activity of MEK mutants found in BRAFV600E inhibitor-resistant melanoma. (a) An immunoblot for MAPK pathway components in 293 FT cells transfected with plasmid DNA containing wild-type MEK, MEKIndel55RT, MEKQ56P, MEKV60E, MEKC121S, MEKP124L, MEKG128V, MEKV154L and BRAFV600E or empty vector controls. Both the transfections and immunoblotting were performed in triplicate. Tubulin was used as a loading control. (b) Densitometry measurements from three experimental replicates showing MEKGF had higher activity than any of the naturally occurring mutants (P<0.05). Although MEK V60, Q56P and 55RT had similar activity, C121s trended toward lower activity, but this was not statistically significant. MEKG128V had lower activity than C121S (P<0.05). P-ERK and P-RSK were not observed for P124L or V154L although P-MEK was detected.