Figure 4.
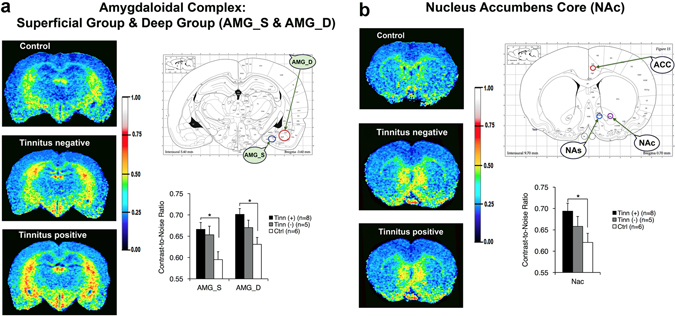
Blast-induced tinnitus (+) rats had higher neural activity in two amygdala subdivisions and in the nucleus accumbens core (NAc) compared to control (ctrl) rats, though there were no significant differences between tinnitus (+) and tinnitus (−) rats. Images were color-coded according to manganese uptake intensity, as defined by the color scale-bar. Color-coded images are shown for a representative tinnitus(+), tinnitus(−) and control (ctrl) rat. A rat brain atlas was used to guide ROI placement. The bar graphs indicate the averaged uptake values per group and brain region. (a) Significantly higher manganese uptake was observed in the superficial and deep amygdalae (AMGS and AMGD) of the tinnitus(+) group, compared to the control group, as well as in the (b) nucleus accumbens core regions (NAC). *Indicates statistical significance (p < 0.05). Atlases were adapted from The Rat Brain In Sterotaxic Coordinates, 4th Edition by Paxinos and Watson (1998) with permission from the publisher.
