Figure 8.
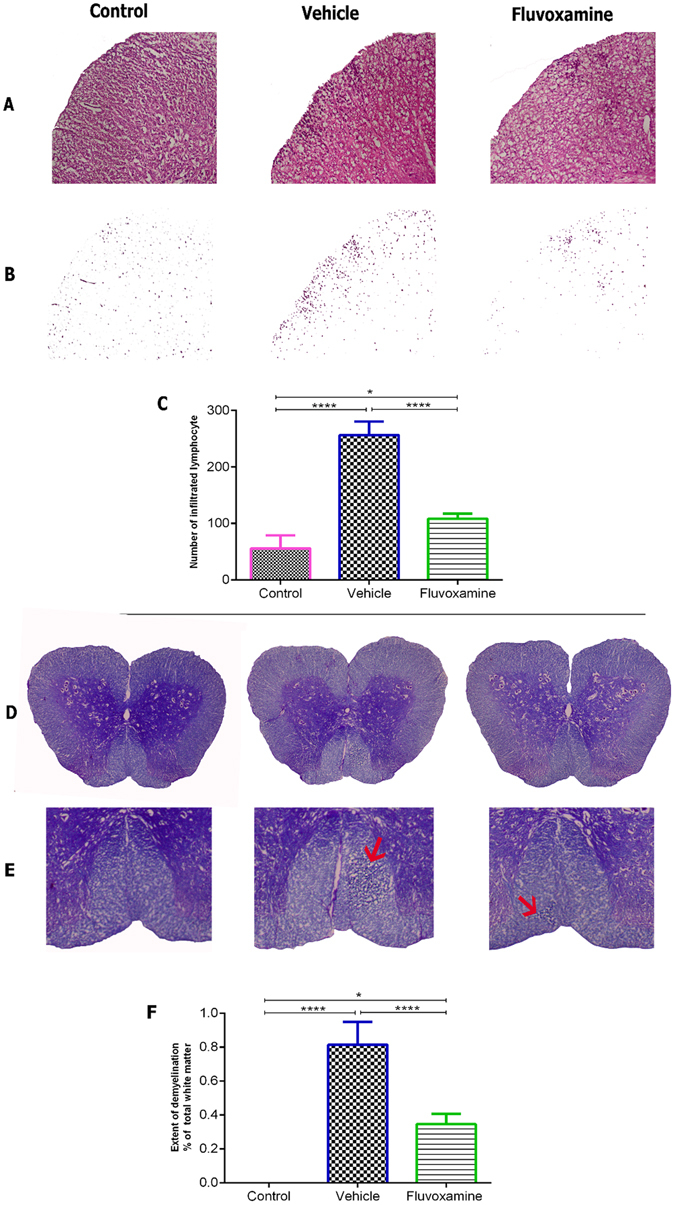
Fluvoxamine treatment enhanced histological outcomes in spinal cords of EAE rats. In order to detect inflammatory infiltration and demyelination, serial sections were analyzed by Hematoxylin and Eosin (A–C) and Luxol Fast Blue staining (D–F). (A) Inflammatory infiltration with extensive perivascular cuffing was limited and decreased in fluvoxamine treated EAE rats, in comparison to EAE control rats. (B) Infiltrated cells are shown without background tissue, a modification from panel (A). (C) Infiltration of immune cells was significantly reduced in fluvoxamine group, compared to vehicle (****p < 0.0001). (D,E) Red arrows indicates demyelination area which is reduced in fluvoxamine group, compared to EAE vehicle rats. (F) Quantitative analysis for percent of demyelination area of total white matter using Luxol Fast Blue staining. Fluvoxamine induced a reduction in demyelination area (0.81%), compared to vehicle (0.34%). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from seven rats per group.
