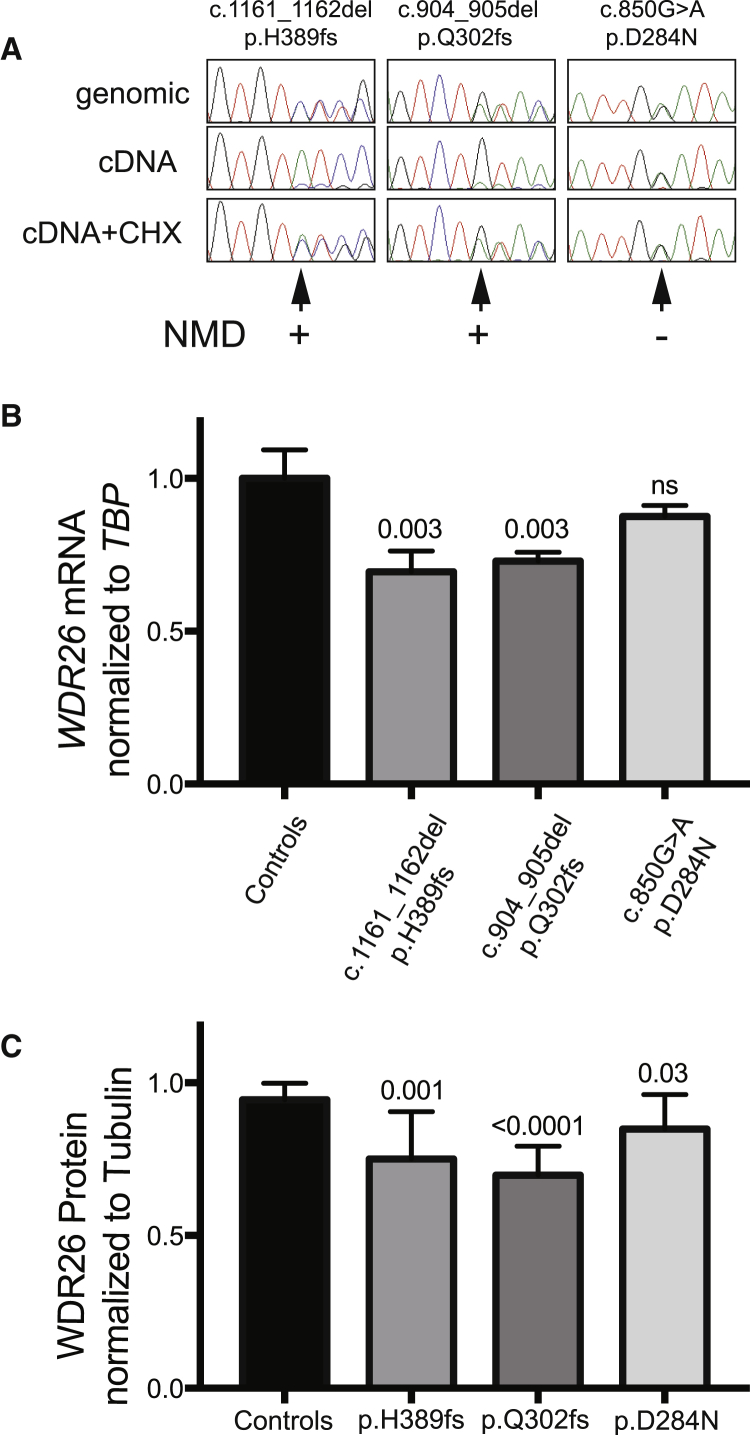
Figure 2.
Effect of WDR26 Mutations on Nonsense-Mediated RNA Decay and Protein Levels
(A) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) analysis. Epstein-Barr-virus-immortalized lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) from subject 2 (c.1161_1162del [p.His389Profs∗6], labeled p.H389fs), subject 4 (c.644T>C [p.Gln302Aspfs∗22], labeled p.Q302fs), and subject 6 (c.850G>A [p.Asp284Asn], labeled p.D284N) were cultured in the presence of 1 mg/mL cycloheximide (CHX) for 6 hr and analyzed by RT-PCR and sequencing for the presence of wild-type and mutant alleles. Sequencing chromatograms for heterozygous genomic DNA as reference, untreated, and CHX-treated conditions are shown, demonstrating the reduced presence of the frameshift alleles but not the missense allele, denoted by an arrow at the location of the mutation and summarized result of the NMD assay (+ or −).
(B) WDR26 RNA expression levels. Consistent with (A), digital droplet-based quantitative RT-PCR of WDR26 mRNA expression normalized to TBP mRNA demonstrated a statistically significant reduction of expression for the frameshift alleles (69% for c.1161_1162del and 73% for c.644T>C) but not for the c.850G>A missense allele (88%).
(C) WDR26 levels were quantified by fluorescent western blotting and normalized to tubulin. Significantly lower WDR26 levels than control levels were noted for each pathogenic allele tested (75% for p.His389Profs∗6, 70% for p.Gln302Aspfs∗22, and 85% for p.Asp284Asn). The mean and SEM, along with unpaired two-tailed p values comparing multiple biological replicates (three for RNA and seven for protein) with controls, are demonstrated for each condition.