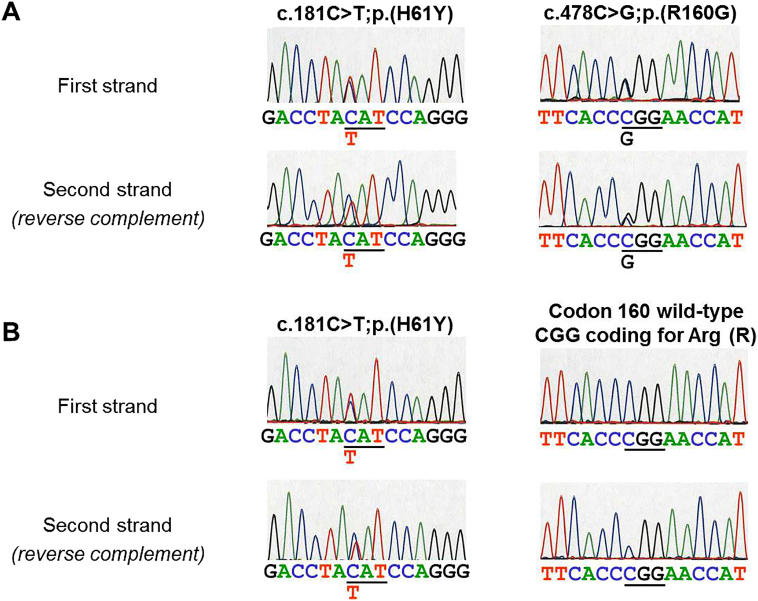
Fig. 2.
SUOX gene DNA sequencing analysis. Panels A and B show sequencing results in the affected child and his mother, respectively. Sequences on both DNA strands are shown, the second strand being reversed complemented. The codon affected by the mutation is underlined. In each case, the normal sequence is listed on top and the mutated nucleotide is indicated below at the corresponding position. The resulting mutation is described at nucleotide and protein levels using HGVS (Human Genome Variation Society) standards.