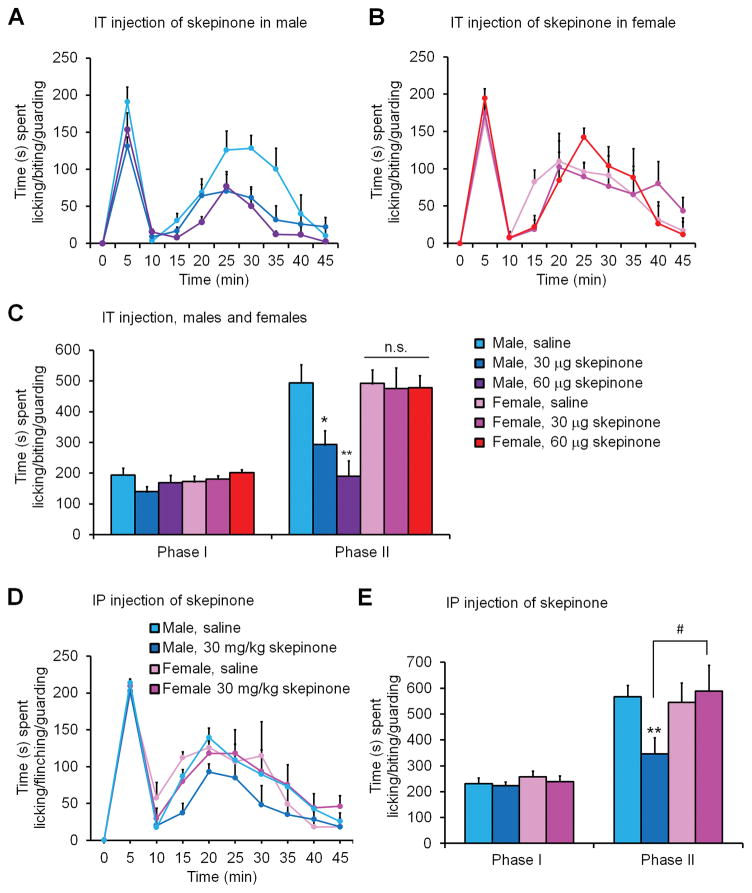
Figure 1. Spinal or systemic inhibition of p38 signaling inhibits spontaneous pain behavior in male but not female mice following formalin injection.
(A–C) IT injection of the p-p38 inhibitor skepinone, 30 minutes prior to intraplantar administration of formalin, dose-dependently reduced spontaneous Phase II pain behavior in male but not female mice. (A,B) Time course of formalin-induced spontaneous pain in males (A) and females (B). (C) Formalin-induced Phase I (0–10 min) and Phase II (15–45 min) responses. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, in comparison to same sex saline control, One-Way ANOVA, n = 6–8 mice per sex per group. n.s., not significant. (D,E) IP administration of skepinone 1 hour prior to formalin injection reduced spontaneous Phase II pain behavior in male but not female mice. (D) Time course of formalin-induced spontaneous pain in males and females. (E) Formalin-induced Phase I (0–10 min) and Phase II (15–45 min) responses. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, in comparison to same sex saline control. #P< 0.05, compared to opposite sex. One-Way ANOVA, n = 6–8 mice per sex per group.