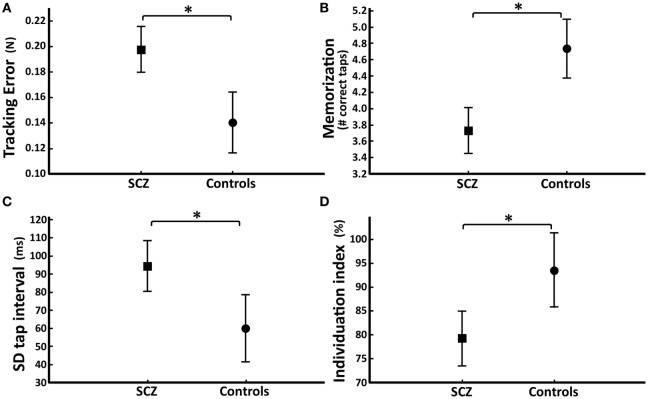
Figure 2.
Group differences in the four key-Finger Force Manipulandum (FFM) scores. Average score (and SD) for each task. Patients (SCZ, represented by squares) vs. control subjects (circles). (A) Tracking error (N) during the finger force-tracking task. (B) Number of correct taps per trial during recall of the sequential finger-tapping task. (C) Tap interval variability (ms) across all conditions of the single-finger-tapping task. (D) Degree of individuation across all fingers for every combination during the multi-finger-tapping task. Compared to control subjects, patients with schizophrenia showed a statistically significant difference (*P < 0.05) in all four key-FFM scores.