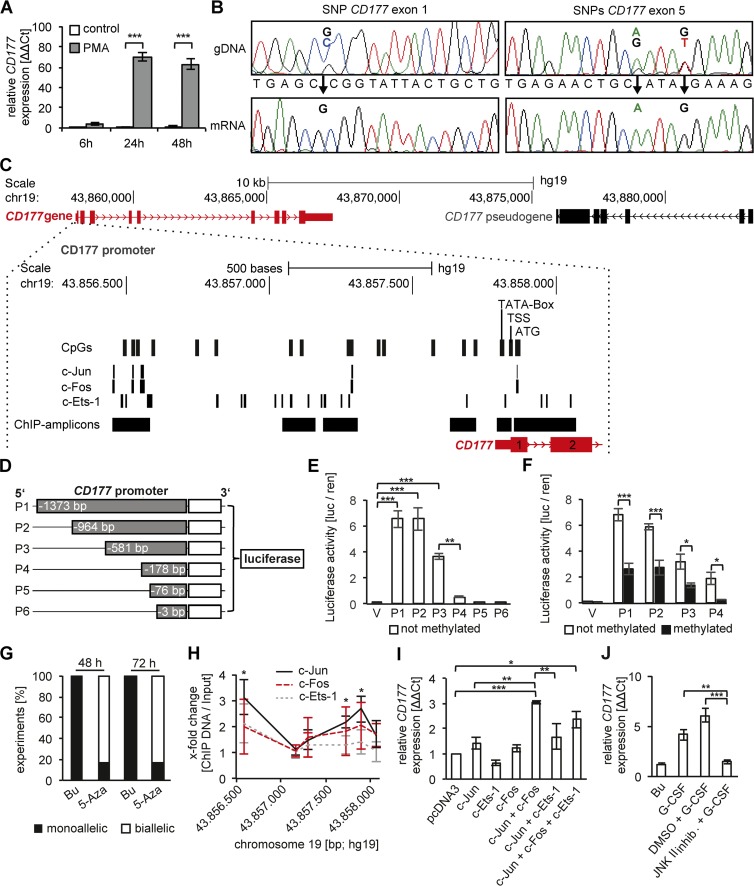
Figure 3.
CD177 gene expression, promoter analysis, DNA methylation, and transcription factor binding in a HeLa cell model. (A) CD177 gene expression was induced in PMA-treated HeLa cells as shown by qRT-PCR (n = 3 independent experiments). (B) CD177 haplotype analysis was performed by Sanger sequencing the genomic DNA (gDNA) and mRNA from HeLa cells (n = 6 independent experiments). Three heterozygous SNPs in the gDNA, one in exon 1 (SNP49 GC) and two in exon 5 (SNP652 AG and SNP656 GT), were found and established monoallelic CD177 gene expression. (C) A schematic overview of the CD177 gene (red), its promoter, and the pseudogene (black) is depicted. The CD177 promoter region is enlarged.16 CpG dinucleotides, the c-Jun, c-Fos, and c-Ets-1 TF binding sites (PROMO database), the TATA box, the transcription start site (TSS), the translation start (ATG), and PCR amplicons of the ChIPed DNA are indicated. (D) The CD177 promoter constructs P1 to P6 were cloned into the CpG-free luciferase vector. (E) Luciferase reporter assays were performed with the unmethylated CD177 promoter constructs P1 to P6 (n = 4 independent experiments). CD177 promoter activity was calculated from the firefly and Renilla luciferase signal. (F) Luciferase reporter assays were performed with P1 to P4 promoter constructs that were either left unmethylated (open bars) or were methylated (black bars) by incubation with methyltransferase (n = 7 independent experiments). (G) PMA-stimulated HeLa cells were treated with buffer (Bu) or 10 µM 5′-Aza-2-deoxycytidine (5-Aza) for 48 and 72 h, respectively (n = 6 independent experiments). Allele expression was analyzed using heterozygous CD177 SNPs (SNP49 rs45441892, SNP652 rs199668750, SNP656 rs200662237) in gDNA and the corresponding mRNA. Black indicates the percentage of experiments where monoallelic CD177 gene expression was detected and white indicates the percentage of experiments where biallelic CD177 allele expression was detected. (H) ChIP assays were performed using antibodies to c-Jun, c-Fos, and c-Ets-1 in PMA-stimulated HeLa cells. (I) Nonactivated HeLa cells were transfected with empty pcDNA3 vector, c-Jun, c-Fos, c-Ets-1, and combinations thereof (n = 3 independent experiments). CD177 gene expression was determined by qRT-PCR. (J) CD177 gene expression by qRT-PCR was assessed in human blood neutrophils stimulated with buffer control (Bu) or 100 ng/ml G-CSF for 90 min, respectively. When indicated, G-CSF–stimulated cells were pretreated with buffer control (DMSO) or 20 µM JNK II inhibitor (CAS 129–56-6) for 30 min, respectively (n = 3 independent experiments). Data in A, E, F, I, and J were displayed as mean ± SEM and were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Data in H were displayed ± SEM and were analyzed using Student’s t test. *, P < 0.05.