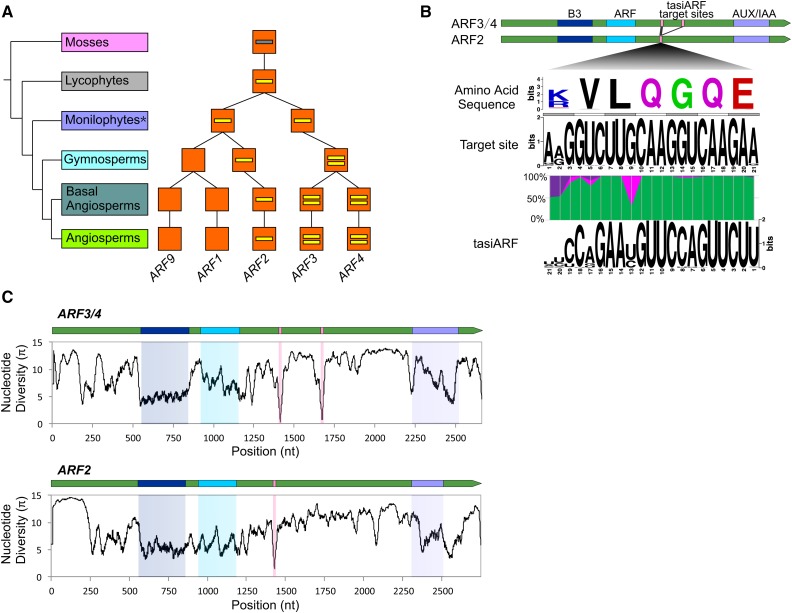
Figure 7.
Evolutionary Diversification of tasiARF Target Sites in ARF Genes.
(A) Evolution of the number of tasiARF target sites in plant ARF genes. The evolutionary route of ARF genes was adapted from Finet et al. (2012). The number of short yellow lines in orange boxes denote the number of tasiARF target sites. The gray line means that there are potential tasiARF target sites in ARF genes in mosses. In monilophytes (marked with an asterisk), some ARF3/ARF4 homologous genes have already evolved two tasiARF target sites.
(B) Sequence features of the target site of tasiARF in ARF genes and their encoded proteins. Gene structures of tasiARF-targeted ARF2/ARF3/ARF4 are displayed on the top, including the encoded protein motifs, with the tasiARF target site indicated as pink bars. The target site encodes a short peptide with a consensus sequence of K/RVLQGQE, as indicated with the encoding sequence. Pairing between tasiARF and its target site is color-coded with A:U/C:G matches denoted in green, G:U matches in purple, and all mismatches in pink.
(C) Distribution of nucleotide diversity along tasiARF-targeted ARF2/ARF3/ARF4 genes, with the encoded functional domains and tasiARF target site marked in colors according to those in (B).