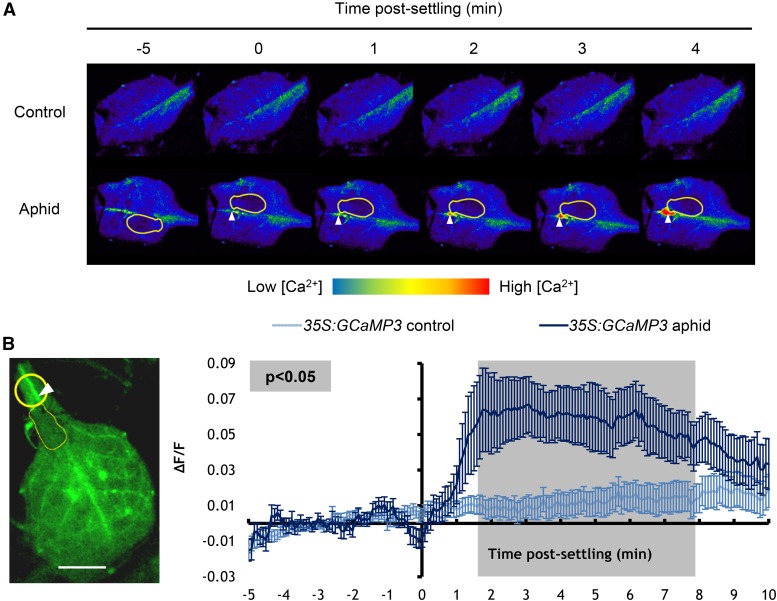
Figure 1.
The GCaMP3 Sensor Detects [Ca2+]cyt Elevations around the Aphid Feeding Site on Detached Leaves.
(A) Representative stereomicroscope images showing GFP fluorescence (color-coded according to the inset scale) around feeding sites of leaves exposed to a M. persicae adult at several time points after aphid settling. Aphid is outlined in yellow. Location of feeding site indicated with an arrowhead.
(B) Left: Stereomicroscope image of a feeding site region (yellow circle) used for the analyses shown on the right (bar = 1 mm). Aphid is outlined in yellow, and location of feeding site is indicated with an arrowhead. Right: Normalized GFP fluorescence (∆F/F) measurements every 5 s around the feeding site from 5 min before until 10 min after settling of an adult aphid. F, average fluorescence intensity prior to aphid settling (baseline); ∆F, difference between measured fluorescence and baseline fluorescence. Error bars represent the se of the mean (n = 34). The average area of the [Ca2+]cyt elevation was 110 ± 18 μm2, and the leading wave front of this elevation traveled radially at 5.9 ± 0.6 μm/s from its center. Gray shading indicates a significant difference between treatments using a Student’s t test within a GLM at P < 0.05.