Figure 5.
The TGD1 TM3-TM5 Region Is Important for the Different Functionality of BdTGD1 in Arabidopsis tgd1-1.
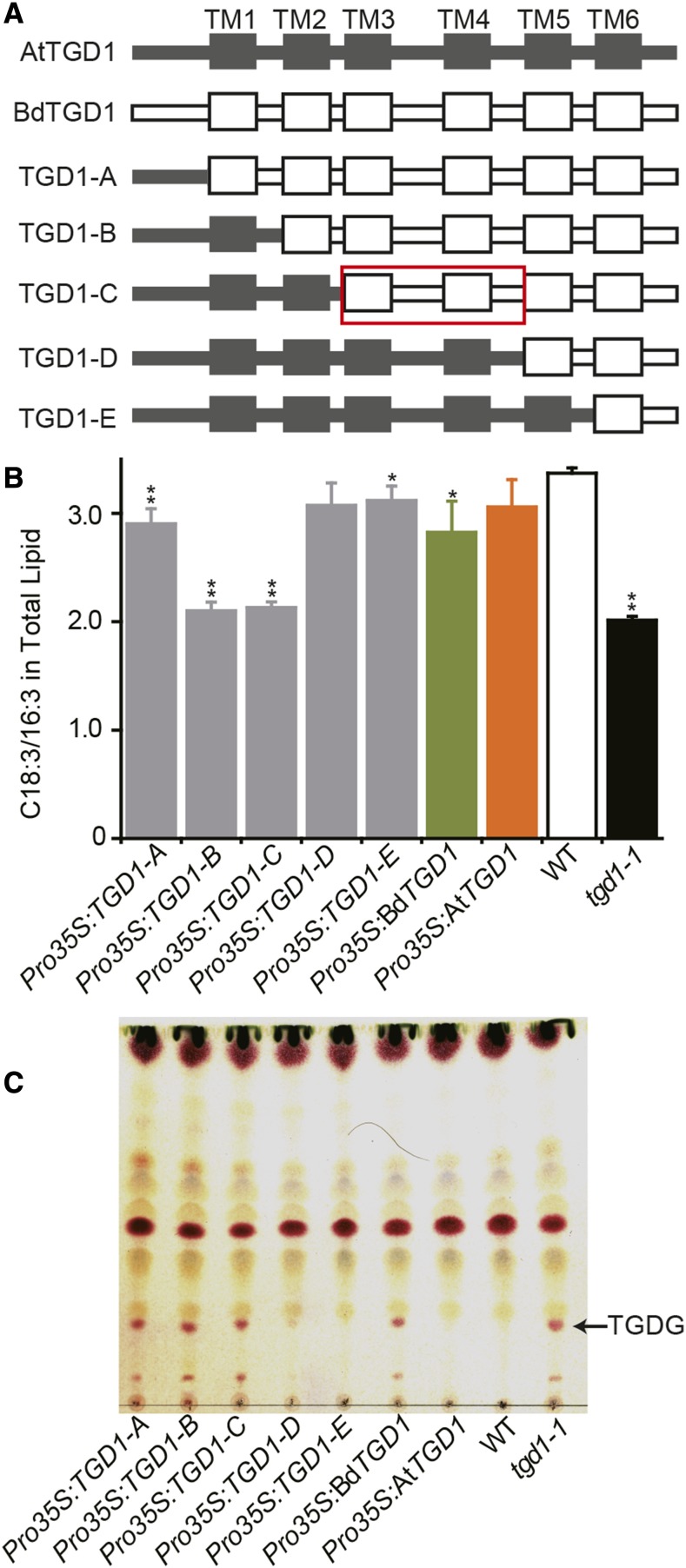
(A) Series of chimeric proteins generated for identification of sequence regions causing functional-divergence between AtTGD1 and BdTGD1. AtTGD1 sequences are gray and BdTGD1 sequences white. The red box indicates the TM3-TM5 region relevant for functional diversity of AtTGD1 and BdTGD1.
(B) Ratios of C18:3/16:3 in total lipids of Arabidopsis leaf tissues. Total lipids were extracted from 4-week-old Arabidopsis leaves. The molar percentages of individual FAs relative to total FAs in each lipid species were quantified using GC-FID of FAMEs. Representative individual plants from three independent lines for each construct (as shown in Supplemental Figure 13) were averaged, and the error bars represent sd. Significant differences compared with the wild type are indicated (Student’s t test): *P < 0.05 and **P ≤ 0.01.
(C) Thin-layer chromatography analysis of polar lipids of a single representative plant for each construct is shown. Glycolipids were visualized by α-naphthol staining. TGDG is indicated.