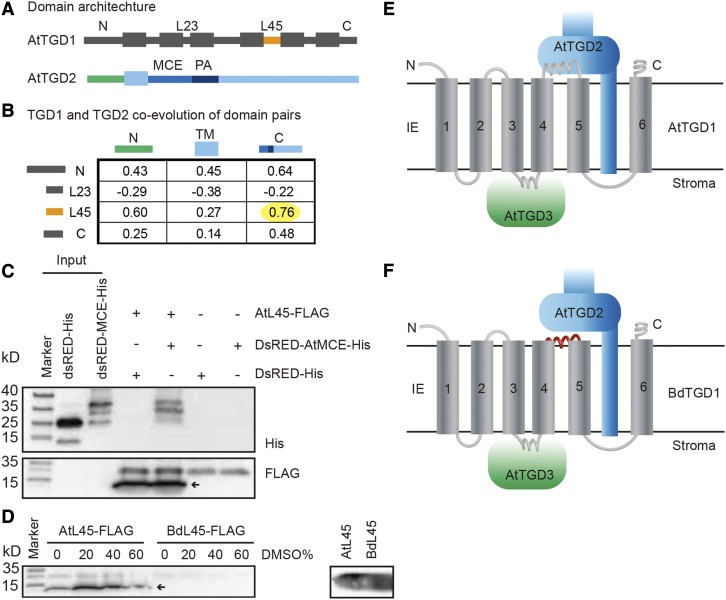
Figure 7.
L45 in TGD1 Coevolved with the MCE Domain in TGD2.
(A) Domain architecture of AtTGD1 and AtTGD2.
(B) Correlation scores by Tol-Mirrortree to assess the coevolution between all possible domains in TGD2 and loops in TGD1 facing the chloroplast intermembrane space. The yellow highlight indicates the highest score among all the analyzed pairs, showing the correlation between the TGD1-L45 and the TGD2-MCE domain.
(C) Coimmunoprecipitation detecting interaction of TGD1-L45 and TGD2-MCE domain. The AtTGD1-L45-FLAG was bound to anti-FLAG magnetic beads and incubated with DsRED-AtTGD2-MCE-His or DsRED-His. Bound proteins were detected by immunoblot using anti-His and anti-FLAG antibodies. The arrow indicates the specific band.
(D) Effect of DMSO on the binding of AtTGD1-L45 or BdTDG1-L45 with anti- FLAG magnetic beads. The left panel shows the binding in different concentrations of DMSO. Bound proteins were detected by immunoblot using anti-FLAG antibody. The right panel shows the amount of AtL45 and BdL45 used in the assay on the left. The arrow indicates the size of the specific band.
(E) Topology of the interaction between components of the Arabidopsis TGD1, 2, 3 complex in the inner envelope membrane (IE). N and C termini are indicated.
(F) Topology of the interaction between components of the heterologous complex containing BdTGD1 and AtTGD2 and AtTGD3 in the Arabidopsis tgd1-1 mutant expressing BdTGD1. The conserved interaction between TGD1 and TGD3 is shown as mentioned in the text. AtTGD1-L45, which faces the intermembrane space of the chloroplast, interacts with the AtTGD2 MCE domain. The L45 motif in BdTGD1, which is unable to interact with the AtTGD2-MCE domain, is shown in red.