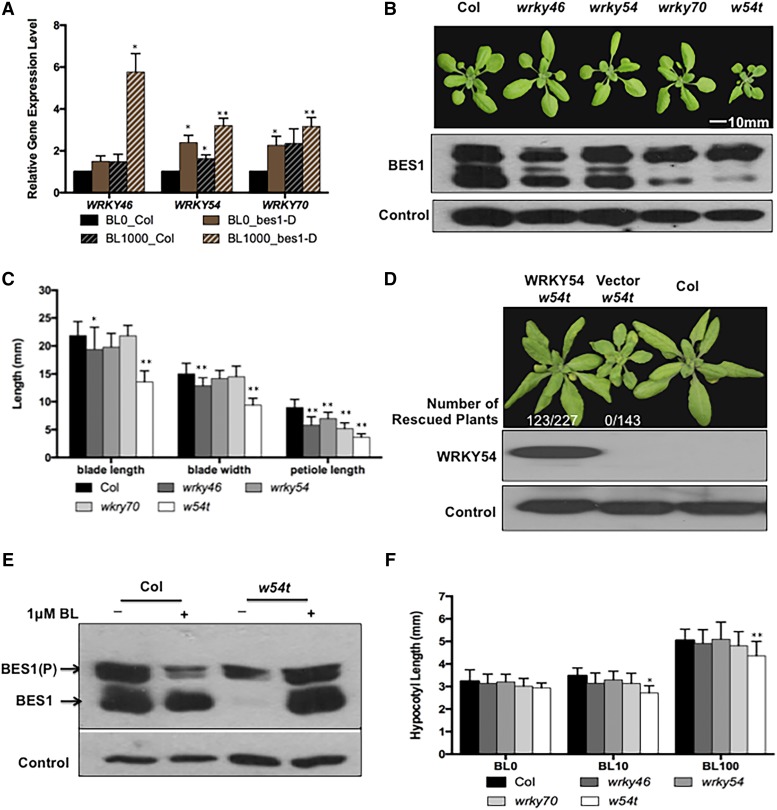
Figure 1.
WRKY46, WRKY54, and WRKY70 Function Redundantly and Play Positive Roles in the BR Pathway.
(A) WRKY46, WRKY54, and WRKY70 mRNA levels were determined in the wild type and bes1-D treated with 1 μM BL or mock control for 2.5 h. The averages and sd were derived from three biological replicates.
(B) Top: The growth phenotype of 3-week-old wild type, wrky46, wrky54, wrky70, and wrky46 wrky54 wrky70 triple mutant (abbreviated as w54t in all figures). Bottom: BES1 protein levels were determined by immunoblot and a loading control was shown at the bottom.
(C) The measurement of blade lengths, blade widths, and petiole lengths of the sixth leaves. Error bars indicate sd, n = 13 (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; Student’s t test).
(D) Transgenic complementation of w54t mutant with PWRKY54:WRKY54-FLAG fusion gene and empty vector as the control. Top: Four-week-old wild-type transgenic plants with vector (w54t) or WRKY54 (w54t) are shown. Bottom: WRKY54 protein accumulation was detected in the transgenic plants by immunoblot with anti-FLAG antibody and HERK1 loading control was shown at the bottom.
(E) BES1 protein accumulation was determined in 4-week-old w54t leaves soaked in 0.5× liquid MS medium with 1 μM BL or DMSO for 30 min.
(F) Hypocotyl lengths of 5-d-old seedlings grown on 0.5× MS medium with 0, 10, and 100 nM BL. Mean was calculated and the sd was also presented. Error bars indicate sd (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; Student’s t test).