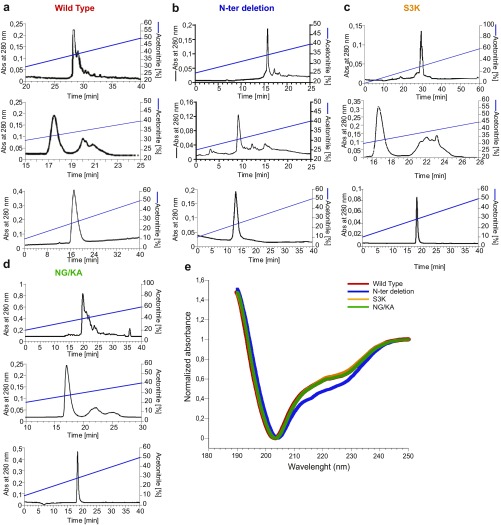
Fig. S3.
Solid-phase synthesis of WT mambaquaretin-1 and its three variants. (A–D) Reverse-phase liquid chromatography of the mambaquaretin-1 WT (A), the N-ter deletion peptide lacking its four first residues (B), the S3K (C), and the NG/KA variants (D). Solvents are A (water, TFA 0.1%) and B (acetonitrile, TFA 0.1%). A–D, Top corresponds to the purification of the crude synthesis on Waters X-bridge C18, 19 250 mm, 10 m, flow of 15 mL/min. The gradients were 10–40% of B in 40 min (mambaquaretin-1 WT), 15–40% of B in 25 min (N-ter deletion peptide), 0–60% of B in 60 min (S3K variant), and 20–60% of B in 40 min (NG/KA variant). A–D, Middle corresponds to the purification of the oxidized peptide performed on a Waters Sunfire 10 m, 10 250 mm. The gradients were 15–40% of B in 25 min (mambaquaretin-1 WT and N-ter deletion peptide), 20–60% of B in 40 min (S3K variant), and 10–40% of B in 30 min (NG/KA variant). A–D, Bottom corresponds to the analytical chromatography of the pure oxidized peptide performed on Waters X-bridge C18, 4.6 150 mm, 3.5 m. Gradient was 10–50% of B in 40 min. (E) Circular dichroism of WT mambaquaretin-1 and its three variants. Absorbance was normalized to fix at 1 the values at 250 nm and at 0 the minima. Size of the symbol equals SD, n = 8–12. Abs, absorbance.