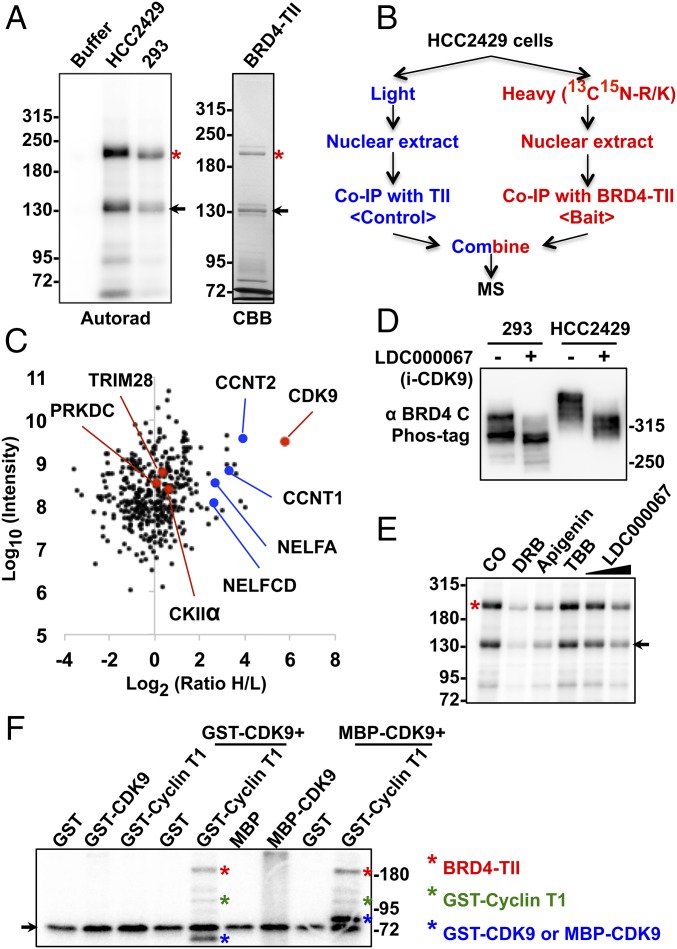
Fig. 2.
CDK9 contributes to BRD4 hyperphosphorylation in NMC. (A) BRD4-TII expressed in E. coli was affinity purified on IgG beads. The beads were either kept in buffer or coimmunoprecipitated with equal amounts of nuclear proteins from HCC2429 or HEK293 cells. After washing, beads were subjected to kinase assay. BRD4-TII samples then were analyzed on SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography (Autorad). BRD4-TII extracted from the beads before kinase assay was analyzed on SDS/PAGE and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB). Asterisks indicate the full-length BRD4-TII. Arrows mark a BRD4-TII fragment purified from E. coli. (B) Flow diagram of the SILAC experiment for identifying BRD4-associated proteins. HCC2429 cells were cultured in light medium (with normal arginine and lysine) or in heavy medium (with 13C- and 15N-labeled arginine and lysine). Nuclear extracts from light-labeled cells were coimmunoprecipitated with beads containing cross-linked TII tag protein, which served as the background control. Nuclear extracts from heavy-labeled cells were coimmunoprecipitated with beads with cross-linked BRD4-TII. After extensive washing, the two samples were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and subjected to mass spectrometry. (C) Plot showing the normalized SILAC ratio intensity. Shown is the SILAC H/L ratio versus the corresponding protein intensity distribution. Red dots indicate BRD4-associated kinases identified with log2(ratio H/L)>0. Blue dots highlight cyclin T1, cyclin T2, and components of the NELF complex. PRKDC encodes the catalytic subunit of the DNA-dependent protein kinase (DNA-PK). The total SILAC data are shown in Dataset S1. (D) HEK293 and HCC2429 cells were treated with DMSO or 5 μM LDC000067 for 1 h. Whole-cell lysates were analyzed on Phos-tag gel and immunoblotted with BRD4 C antibody. (E) BRD4-TII expressed in E. coli was affinity purified on IgG beads and used to coimmunoprecipitate nuclear proteins from HCC2429 cells. Equal amounts of immunocomplexes were subjected to in vitro kinase assay in the presence of DMSO, 50 μM DRB, 50 μM apigenin, 50 μM TBB, or 2 μM or 10 μM LDC000067. The samples then were analyzed on SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. The asterisk indicates the full-length BRD4-TII. The arrow marks a BRD4-TII fragment purified from E. coli. (F) BRD4-TII expressed in E. coli was used to coimmunoprecipitate GST, GST-CDK9, GST-cyclin T1, MBP (Maltose-binding protein), or MBP-CDK9 from E. coli lysates as indicated. The immunocomplexes were subjected to in vitro kinase assay. The samples were resolved on SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. Phosphorylated BRD4-TII, cyclin T1, and CDK9 are marked with red, green, and blue asterisks, respectively. The arrow marks a nonspecific band present in all the samples. See also Fig. S2, Table S1, and Dataset S1.