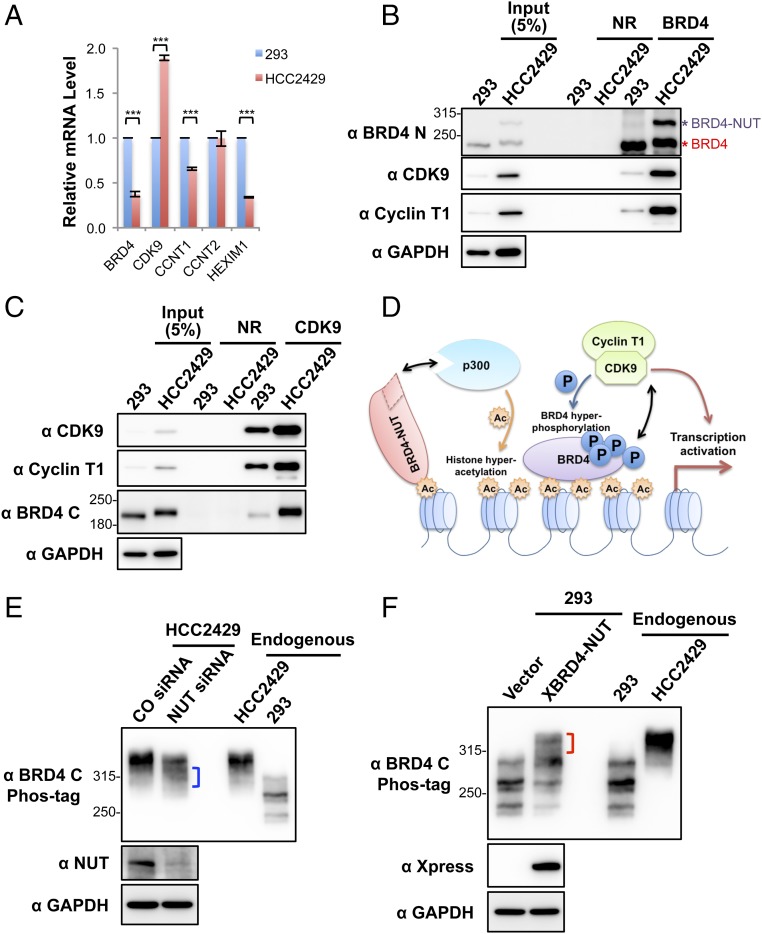
Fig. 3.
Enrichment of CDK9 in BRD4–NUT–induced hyperacetylated chromatin foci causes BRD4 hyperphosphorylation. (A) Relative mRNA levels in HEK293 and HCC2429 cells were measured by RT-qPCR and normalized to GAPDH mRNA levels. The values for HEK293 mRNA levels were set as 1. Values represent the average of three independent experiments; error bars indicate SD. ***P < 0.001. (B) Nuclear extracts of HEK293 and HCC2429 cells were immunoprecipitated with normal rabbit (NR) or Brd4 N-terminal domain (Brd4 N) antibodies. The samples were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (C) Nuclear extracts of HEK293 and HCC2429 cells were immunoprecipitated with normal rabbit (NR) or CDK9 antibodies. The samples were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. (D) The mechanisms underlying BRD4 hyperphosphorylation in NMC. BRD4-NUT recruits and activates p300 to induce histone hyperacetylation in discrete chromatin foci in NMC. This hyperacetylation leads to the sequestration and enrichment of BRD4 and associated P-TEFb in the hyperacetylated chromatin domains, leading to BRD4 hyperphosphorylation. (E) HCC2429 cells were transfected with control (CO) or NUT siRNA. At 30 h posttransfection, whole-cell lysates were analyzed on Phos-tag or SDS/PAGE gels and were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The bracket marks the BRD4 bands with reduced levels of phosphorylation. (F) HEK293 cells were transfected with the empty vector control or a construct expressing Xpress-tagged BRD4-NUT (XBRD4-NUT). At 2 d posttransfection, whole-cell lysates were analyzed on Phos-tag or SDS/PAGE gels and were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. The bracket marks the hyperphosphorylated BRD4 bands. In both E and F, lysates from untransfected HCC2429 and HEK293 cells were also loaded on the same Phos-tag gel to show the endogenous BRD4. See also Fig. S3.