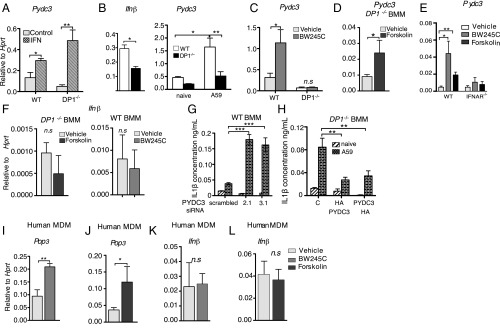
Fig. 6.
Pydc3 inhibits inflammasome function. BMMs from WT, DP1−/−, or IFNAR−/− mice (A–H) or MDMs from human blood (I–L) were prepared. (A) Pydc3 mRNA levels were measured in BMMs treated with IFN-β or PBS (control) for 48 h. (B) Ifnβ and Pydc3 mRNA levels were measured in A59-infected WT or DP1−/− cells. (C, D, and F) Pydc3 (C and D) and Ifnβ (F) mRNA levels were measured in uninfected WT or DP1−/− BMMs following treatment with BW245C (C and F), forskolin (D and F), or vehicle for 48 h. (E) WT or IFNAR−/− BMMs were treated with BW245C, forskolin, or vehicle, and Pydc3 mRNA levels were quantified using qRT-PCR. (G and H) BMMs were infected with A59 following either siRNA-mediated knockdown in WT BMMs (G) or overexpression of Pydc3 in DP1−/− BMMs (H), and IL1β in cell supernatants was quantified by ELISA. MDMs were generated from human PBMCs as described in Materials and Methods. (I–L) Pop3 (I and J) or Ifnβ (K and L) mRNA levels following BW245C treatment (I and K) or forskolin treatment (J and L) were quantified using qRT-PCR. Data shown represent the mean ± SEM of two independent experiments; n = 4 samples per group; **P < 0.01; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, Mann–Whitney U test; n.s., not significant. MDM, monocyte-derived macrophages.