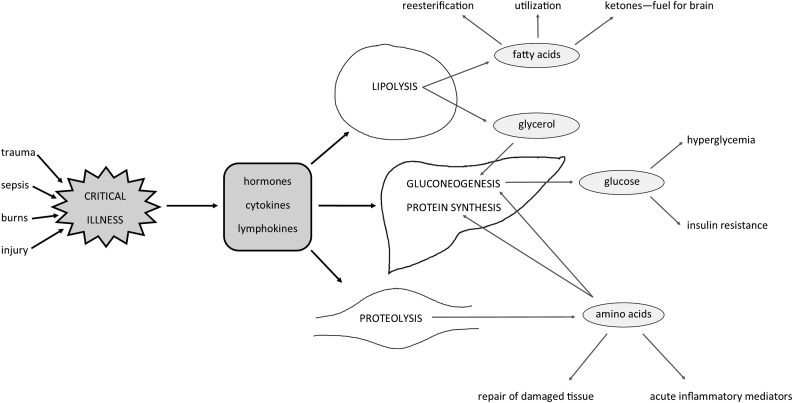
FIGURE 1.
Metabolic response in critical illness. All mediators released during the stress response counteract insulin action. This leads to protein catabolism, lipolysis, and gluconeogenesis. In general, protein catabolism predominates. Amino acids released from muscles are deaminated in the liver and used for gluconeogenesis or converted into inflammatory proteins. During lipolysis, TGs are hydrolyzed to FFAs and glycerol in the adipose tissue. Glycerol is additionally used for gluconeogenesis in the liver, and FAs may be used in the liver and muscle, converted to ketone bodies, or re-esterified. Because of gluconeogenesis, hyperglycemia and insulin resistance occurs.