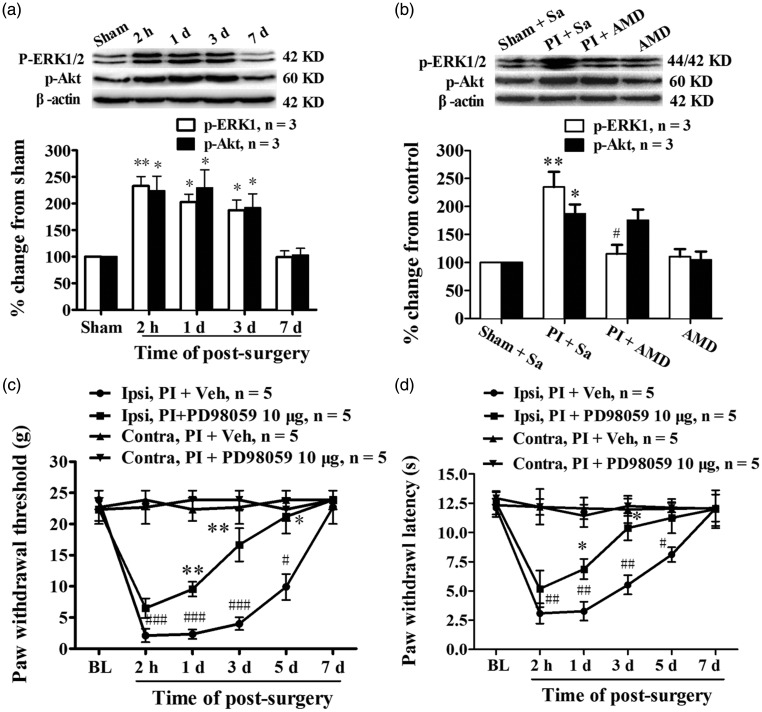
Figure 5.
ERK and PI3K-Akt signaling were activated in spinal cord after PI, and CXCL12/CXCR4-mediated postsurgical pain depended on ERK activation. (a) Western blotting data showing the time course of ERK and Akt activation in spinal cord after PI. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus sham group, one-way ANOVA. (b) Prior i.t. administration of AMD3100 prevented ERK, but not Akt, activation in spinal cord after PI. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus sham group. #P < 0.05 versus PI + Vehicle (Veh) group, one-way ANOVA. (c, d) Repetitive given rats of PD98059, a specific ERK kinase inhibitor, intrathecally prevented the reduction of PWT (c) and PWL (d) after PI. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 versus PI + Veh group, Student's t-test. #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01; ###P < 0.001 versus baseline value, two-way ANOVA.