Figure 3.
Increase in Transduction Efficacy Is Reflected by Increased GDNF Transgene Levels
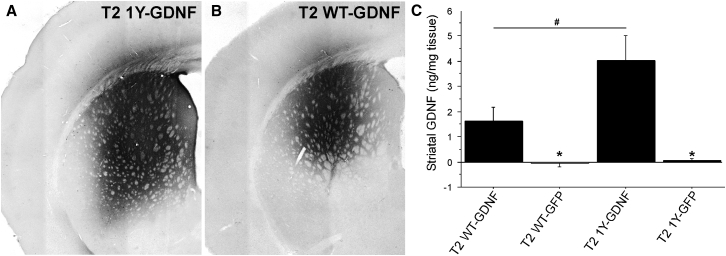
An AAV genome containing an expression cassette encoding human glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) was packaged into T2 WT or T2 1Y, and the same capsid mutants with a GFP expression cassette were utilized as controls. Adult Sprague-Dawley rats received unilateral intrastriatal injections of either vector (2 μL of 1.2 × 1012 vector genomes/μL for all viruses); 1 month later, the striatum was collected for ELISA protein measurements and histology. (A and B) Representative images of striatal GDNF immunoreactivity from animals injected with T2 1Y-GDNF (A) or T2 WT-GDNF (B). (C) ELISA protein measurements of the human GDNF transgene levels in the AAV-injected striatal samples from animals injected with either T2 WT-GDNF (n = 8), T2 WT-GFP (n = 4), T2 1Y-GDNF (n = 7), or T2 1Y-GFP (n = 4). Transduction with T2 1Y-GDNF resulted in significantly higher striatal GDNF levels than that produced by T2 WT-GDNF (#p = 0.01). No GDNF was detected in either GFP control-treated subject. *p = 0.01 versus T2 WT-GDNF and p = 0.001 versus T2 1Y-GDNF. Error bars represent the mean + SD.