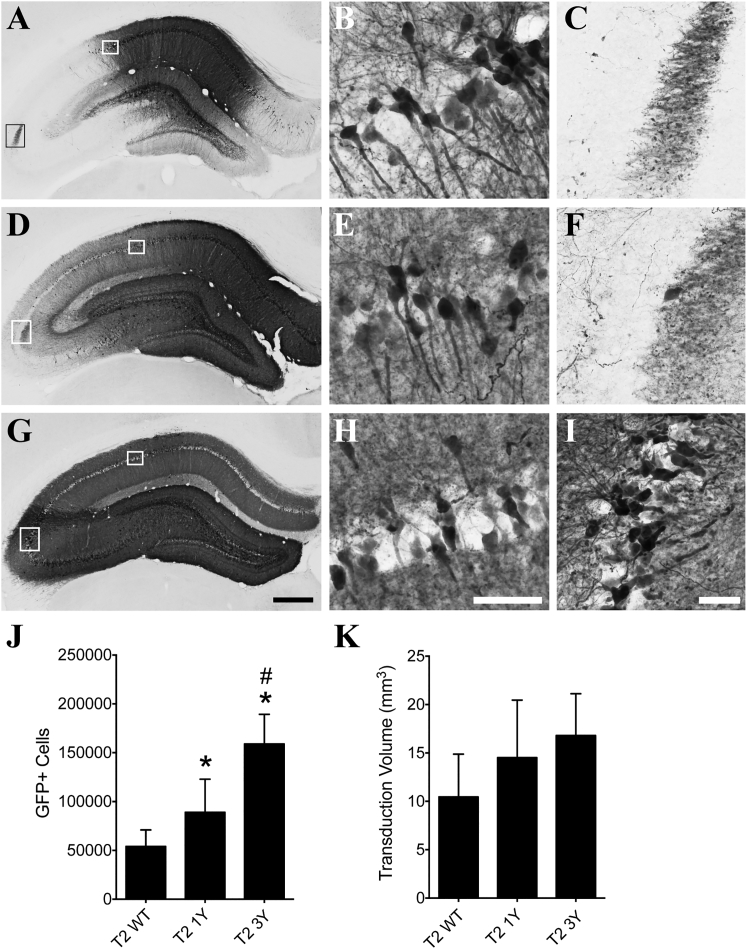
Figure 4.
AAV2 Capsid Mutations Significantly Improve Transduction of the Hippocampus
Adult Sprague-Dawley rats received unilateral intrahippocampal injections of either T2 WT, T2 1Y, or T2 3Y virus (2 μL of 1.2 × 1012 vg/μL). One month later, the animals were sacrificed and processed for transgene (GFP) immunoreactivity. (A–C) Representative micrographs of T2 WT transduction in the hippocampus; white boxes in (A) are regions shown in (B) and (C). (D–F) Representative micrographs of T2 1Y mutant AAV transduction throughout the hippocampus; white boxes in (D) are regions shown in (E) and (F). (G–I) Representative micrographs of T2 3Y transduction throughout the entire hippocampus; white boxes in (G) indicate regions shown in (H) and (I). Note that all viruses transduce dentate granule cells (A, D, and G). (J) Unbiased stereological quantitation of GFP+ neurons showed that the T2 1Y virus (n = 9) transduced significantly more cells than the T2 WT virus (n = 8), and the T2 3Y virus (n = 7) transduced significantly more than T2 WT and T2 1Y in the hippocampus (*p < 0.05 versus T2 WT and #p < 0.05 versus T2 1Y, one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s post hoc). (K) Unbiased stereological quantitation of the transduction volume showed a trend toward a difference among the T2 WT (n = 8), T2 1Y (n = 9), and T2 3Y (n = 7) viruses (p = 0.065, one-way ANOVA) in the hippocampus. Scale bars, 500 μm (G, also applies to A and D); 100 μm (H, also applies to B and E); 50 μm (I, also applies to C and F).