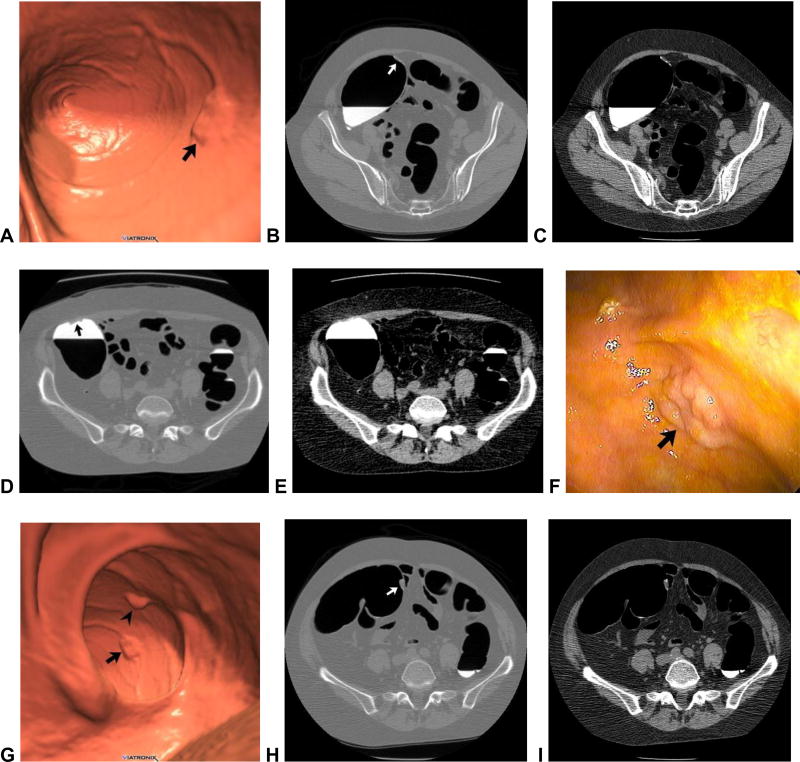
Figure 1. Flat and sessile cecal polyps (tubulovillous adenomas) at CTC.
Supine 3D endoluminal (A), 2D polyp window (B), and 2D soft tissue (C) views from CTC show a 2-cm flat lesion (arrows) within the cecum. Not the thin coating of contrast clinging to the flat lesion, but not the surrounding normal mucosa. Prone 2D image with polyp window (D) shows the flat lesion (arrow) submerged under the opacified fluid. Although the iodine tagging allows for detection of submerged polyps, a broad window must be used, as the lesion may be obscured on a soft tissue window (E). Image from OC (F) confirms the flat lesion (arrow). Additional 3D endoluminal CTC image (G) shows a conspicuous 1.3-cm sessile polyp (arrow) adjacent to the flat lesion (arrowhead). The ileocecal valve is seen across from the polyps. Supine 2D images (H and I) confirm the soft tissue nature sessile polyp (arrow), and also show contrast coating. The ileocecal valve is also well seen at this level.