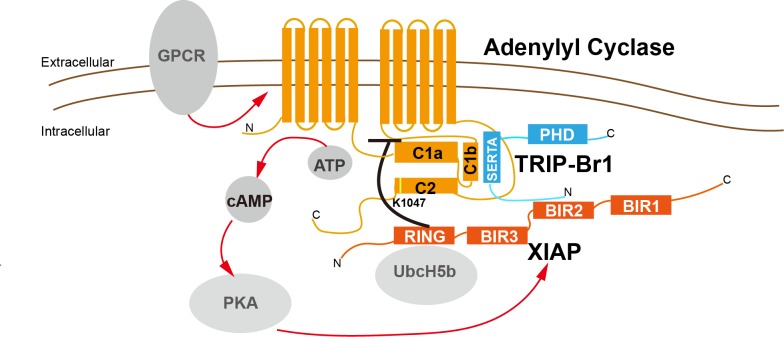
Figure 9. A model depicting a general negative-feedback mechanism of ubiquitination and degradation of multiple AC isoforms.
The SERTA domain of TRIP-Br1 binds to the C1b catalytic domain of AC1 or other AC isoforms and subsequently recruits XIAP, which, together with the E2 enzyme UbcH5b (or UbcH5a or UbcH5c) (Nakatani et al., 2013; Mace et al., 2008), ubiquitinates K1047 in AC1 or an equivalent Lys residue in other AC isoforms. The N-terminus of TRIP-Br1 interacts with XIAP, probably with its BIR2 domain (Hong et al., 2009), and the Ring domain of XIAP interacts with UbcH5b (Nakatani et al., 2013; Mace et al., 2008). The ubiquitination of ACs leads to their endocytosis and degradation. Sustained AC activation and cAMP production under catecholamine stress increase XIAP protein expression through PKA, and elevated XIAP protein expression subsequently dstabilizes ACs and eventually lows cAMP production/signaling. Red arrow, stimulatory effect; black dash: inhibitory effect.