Figure 4. AKG supplementation affects intestinal innate immunity may through intestinal microbiota.
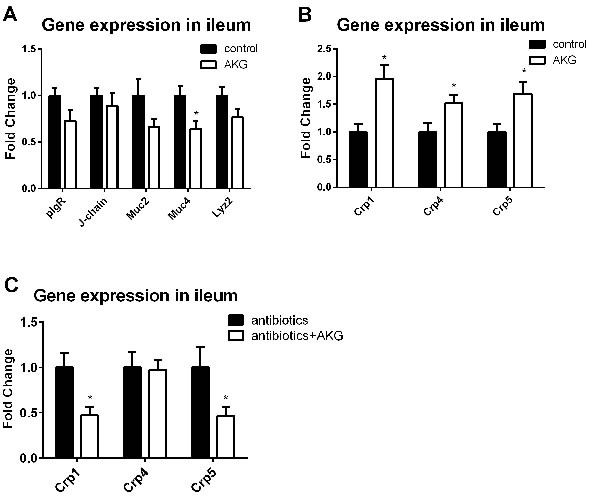
A. Expression of innate immune factors (Il-17, Ifn-γ, pIgR, J-chain, Muc2, Muc4, Crp1, Crp4, Crp5, and Lzy2) in the control group and AKG group (n = 12). Mice in control group received normal drinking water for 2 weeks, while mice in AKG group received AKG supplementation water (10g/L). B. Expression of α-defensins (such as Crp1, Crp4, and Crp5) in the antibiotics group and antibiotics+AKG group (n = 12). Mice in antibiotics group received antibiotics-supplemented drinking water (1 g/L ampicillin; 450 mg/L streptomycin; 200 mg/L gentamicin) for 2 weeks, while mice in AKG group received water supplemented with antibiotics and AKG (10g/L AKG; 1 g/L ampicillin; 450 mg/L streptomycin; 200 mg/L gentamicin). The statistical analyzing between two groups was performed by the Student's t-test. *Indicates a statistically significant difference between the two groups (P < 0.05). Abbreviations: pIgR, polymeric immunoglobulin receptor; J-chain, immunoglobulin joining chain; Muc2, mucin-2; Muc4, mucin-4; Lzy2, lysozyme 2; Crp1, cryptdins-1; Crp4, cryptdins-4; Crp5, cryptdins-5.
