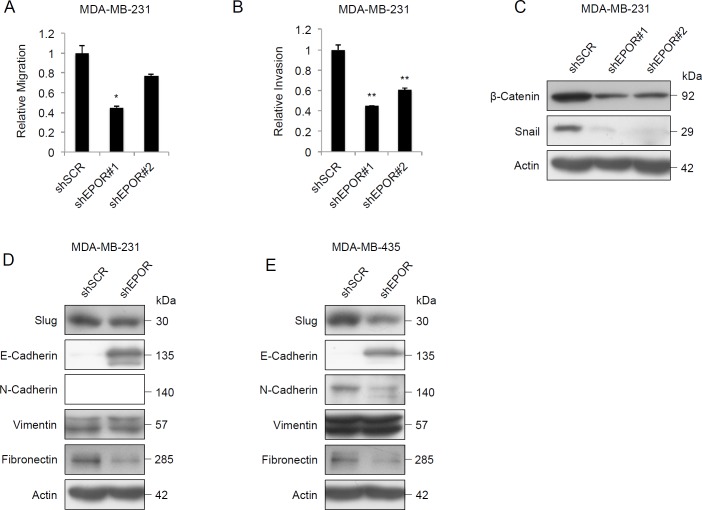
Figure 4. Effect of EPOR knockdown on migration, invasion and EMT protein expression.
A. In vitro migration in MDA-MB-231-shSCR, MDA-MB-231-shEPOR#1 and MDA-MB-231-shEPOR#2 breast tumor cells, measured as the relative migration through membrane inserts with 8 μm pore size, after 24 hours. Data shown are mean fold changes ± SEM for three independent replicates, *p < 0.05, paired t test. B. In vitro invasion in MDA-MB-231-shSCR, MDA-MB-231-shEPOR#1 and MDA-MB-231-shEPOR#2 cells, measured as the relative invasion through Matrigel-coated invasion chamber inserts with 8 μm pore size. Cells seeded in the upper chamber were allowed to migrate through a Matrigel-coated membrane for 24 hours using fetal bovine serum as chemoattractant. Data shown are mean fold changes ± SEM for three independent replicates, **p < 0.01, paired t test. C. Immunoblot of β-catenin and Snail in MDA-MB-231-shSCR, MDA-MB-231-shEPOR#1 and MDA-MB-231-shEPOR#2 cells. Total protein was harvested 72 hours after viral transduction. (D,E) Immunoblots of Slug, E-cadherin, N-cadherin, Vimentin and Fibronectin in D. MDA-MB-231-shSCR and MDA-MB-231-shEPOR#1 cells and in E. MDA-MB-435-shSCR and MDA-MB-435-shEPOR#1 cells. Total protein was harvested 72 hours after viral transduction.