Figure 4. Smad4 is a novel direct downstream target gene of OVOL2.
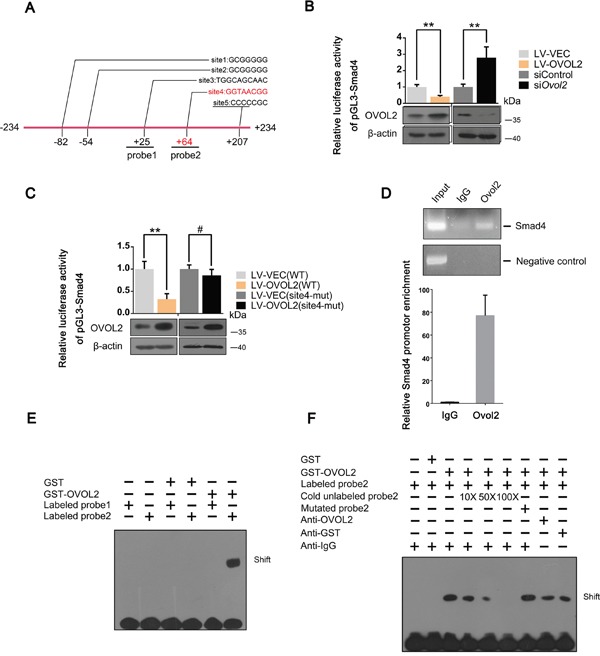
(A) Schematic depiction of the Smad4 promoter with several conserved putative Ovol2 binding sites indicated. Sites 1,2,3,5 represent putative binding sites according to classical yet controversial binding sites, while site 4 represents the bona fide site. (B) Effects of OVOL2 overexpression or Ovol2 knockdown on Smad4 promoter activity, as determined by using the pGL3-basic luciferase reporter cassette in 4T1 cells. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P< 0.01. (C) Effects of OVOL2 overexpression on wild-type Smad4 promoter and mutated Smad4 promoter activities, as determined by using the pGL3-basic luciferase reporter cassette in 4T1 cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. **P< 0.01, #P > 0.05. (D) ChIP assay of endogenous Ovol2 for the Smad4 promoter using semi-quantitative RT-PCR (top) and quantitative real-time PCR (bottom) analyses. A region 10 kb upstream of the Smad4 promoter was used as a negative control. For the RT-PCR analysis, a representative experiment is presented. For the quantitative real-time PCR analysis, the data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (E) Comparison of the binding affinity of GST-OVOL2 for probe1 and probe2 (probe1 was designed according to the putative OVOL2 binding site 3, and probe2 was designed according to the putative OVOL2 binding site 4) using an EMSA assay. (F) Further analysis of the binding affinity of GST-OVOL2 to probe2 using an EMSA assay.
