Figure 2. HIPK2/PP1Cα interacts with Dvl3 and is required for Dvl3 protein de-phosphorylation in HCC cells.
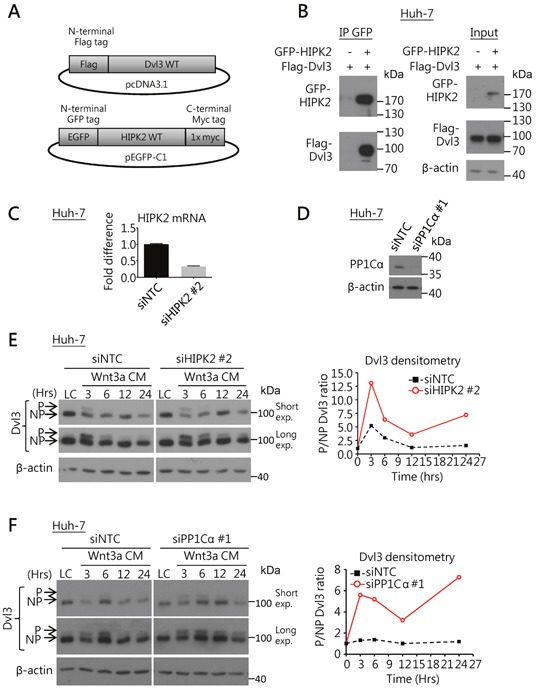
(A) Schematic diagrams for the DNA constructs used in the Co-IP experiment. (B) Co-IP experiment showed the binding of HIPK2 and Dvl3 proteins in Huh-7 cells. The result of one representative trial of the 3 independent experiments is shown. (C) Efficient knockdown of HIPK2 by siRNA in Huh-7 cells as compared to NTC. (D) Efficient knockdown of PP1Cα by siRNA in Huh-7 cells as compared to NTC. (E) Knockdown of HIPK2 sustained Wnt3a-induced phosphorylation of Dvl3 in Huh-7 cells. The cells were treated with Wnt3a conditioned medium (Wnt3a CM) for the indicated time periods upon transfection of the siRNA. Western blots of both short and long exposure (exp.) are shown (left). Densitometry showing the ratio of the phosphorylated (P-) to the non-phosphorylated (NP-) Dvl3 (P/NP) plotted relative to the respective L-cell control medium (LC) upon the knockdown of HIPK2 (right). (F) Knockdown of PP1Cα sustained the Wnt3a-induced phosphorylation of Dvl3 in Huh-7 cells. The cells were treated with Wnt3a-conditioned medium (Wnt3a CM) for the indicated periods of time upon transfection of the siRNA. Western blots of both short and long exposure (exp.) are shown (left). Densitometry showing the ratio of the P- to the NP-Dvl3 (P/NP) plotted relative to the respective L-cell control medium (LC) upon the knockdown of PP1Cα (right).
