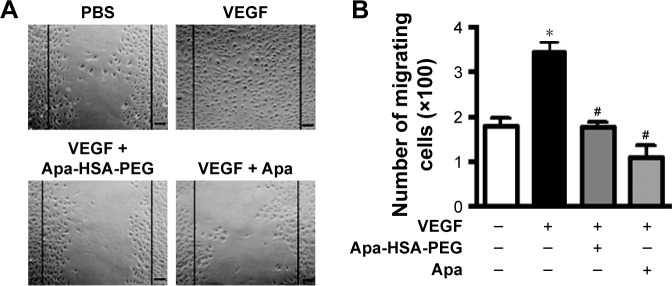
Figure 2.
Apa-HSA-PEG nanoparticles inhibit VEGF-induced wounding migration of human endothelial cells.
Notes: (A) Representative images of scratch wounding migration and (B) quantification of migrating cell number. Confluent HUVEC monolayers grown in six-well plates were scratched and treated with PBS, Apa (1 µM), or Apa-HSA-PEG nanoparticles containing an equivalent amount of Apa in the presence or absence of rhVEGF (100 ng/mL) for 24 h. Scratch wounding migration was quantified by determining the number of cells that migrated from the wound edges (black lines). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (*P<0.05 vs PBS control and #P<0.05 vs VEGF only, n=5). Scale bars =50 µm.
Abbreviations: Apa-HSA-PEG, apatinib-loaded human serum albumin-conjugated polyethylene glycol; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cell; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; Apa, apatinib; rhVEGF, recombinant human VEGF; SEM, standard error of the mean.