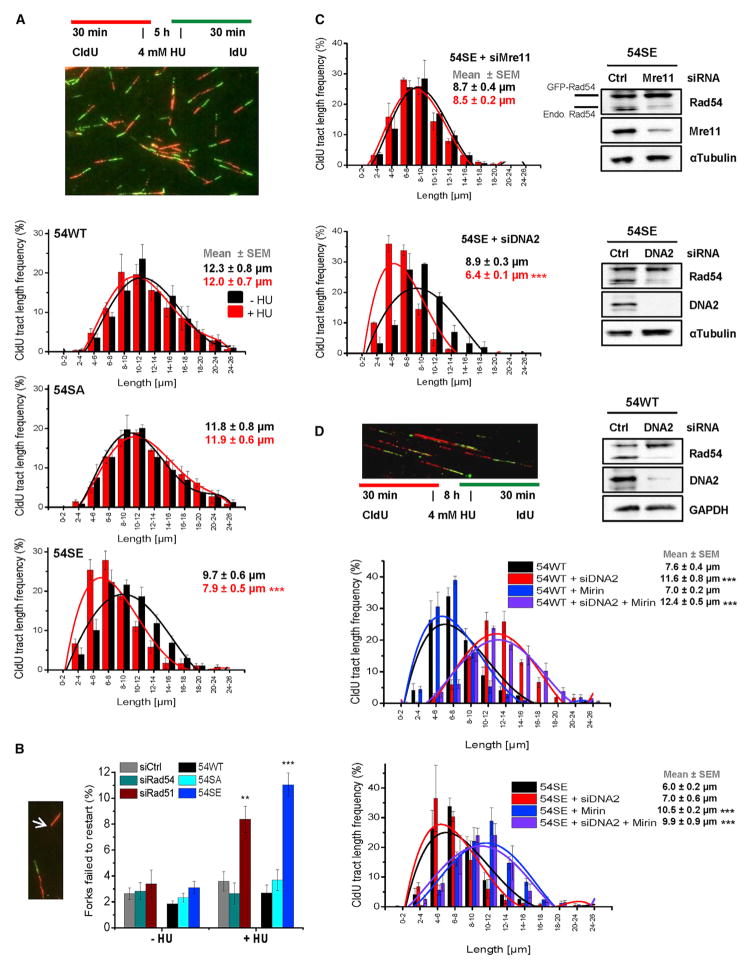
Figure 6. Rad54 Phosphorylation during S Phase Causes Degradation of Stalled Replication Forks.
(A) DNA degradation at stalled forks in Rad54 mutants analyzed by the DNA fiber assay. CldU was added to siRad54-treated HeLa clones, followed by HU treatment and an IdU pulse. CldU-positive DNA fibers were analyzed and categorized according to size. The mean ± SEM for each category separately and for all categories together are shown (n = 5).
(B) Replication fork recovery in Rad54 mutants. HeLa clones were treated with siRad54 and HeLa cells with siCtrl, siRad54 or siRad51 prior to the experiment which was performed as in (A). CldU-positive fibers without a flanking IdU signal were scored (indicated by arrow). Mean ± SEM (n = 5).
(C) DNA degradation at stalled forks in the 54SE mutant analyzed by the DNA fiber assay. CldU was added to siRNA-treated 54SE cells, followed by HU treatment and an IdU pulse. The analysis was performed as in (A). Mean ± SEM (n = 3).
(D) DNA degradation at stalled forks in 54WT or 54SE cells analyzed by the DNA fiber assay. HeLa clones were treated with siRNAs and/or Mirin. CldU was added, followed by HU treatment and an IdU pulse. The analysis was performed as in (A). Mean ± SEM (n = 3).