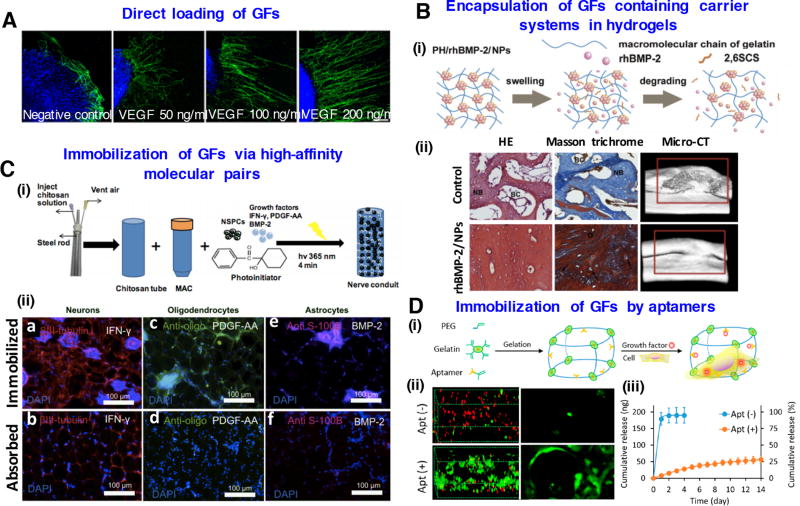
Figure 3.
Biofunctionalization of hydrogels for regenerative engineering: (A) Direct loading of VEGF growth factors in gelatin-based hydrogels enhances axon outgrowth of neuron cells. Reproduced with permission [121]. Copyright 2014, John Wiley & Sons. (B) Encapsulation of GFs containing carrier systems in hydrogels. (i) Schematic representation of rhBMP-2 release from nanoparticles into hydrogels (i) Histological and micro-CT evaluation of bone formation of rhBMP-2 containing hydrogels at 12 weeks. Images modifies from [127] with permission of Elsevier. (C) Immobilization of GFs via high-affinity molecular pairs. (i) Creation of spinal cord regenerative conduits incorporating encapsulated neural stem cells and immobilized differentiation factors. (ii) Immunostaining results after 4-week implantation showing directed differentiation to neurons, oligodendrocytes and astrocytes. Images reprinted from [144] with permission of Elsevier. (D) Immobilization of growth factors by aptamers in PEG-gelatin hydrogels. (i) Schematic of chimeric hydrogel synthesis. (ii) Confocal microscopy images of live and dead cells and cell morphology in the hydrogels. (iii) VEGF release profile from the hydrogels with or without aptamer modification. Images reprinted from [153] with permission of American Chemical Society.