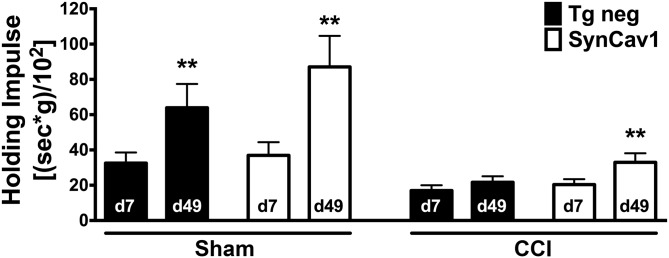
Figure 3.
SynCav1 Tg mice exhibit improved motor function recovery after brain trauma. CCI resulted in a significant decrease in holding impulse in both Tg-negative (black bars) and SynCav1 mice (open bars) on d 7. When comparing recovery between d 7 and 49 with a paired Student’s t test, all groups except for CCI/sham significantly improved their motor recovery as indicated by a significant increase in the holding impulse [body weight (g) × hanging time (s)/102]. Data (n = 11–22 mice/group) are presented as means ± sem. **P < 0.05.