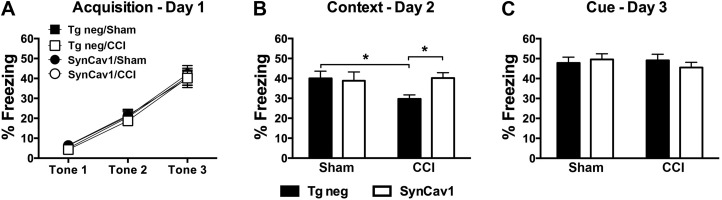
Figure 4.
SynCav1Tg mice show preserved contextual fear learning and memory months after brain trauma. A) Both groups showed similar acquisition in response to CS 2 mo post-CCI. This was reflected in a significant effect of time during the repetitive exposure of the tone/shock pairings, with no significance for gene or time × gene interaction. B) On d 2, contextual reexposure demonstrated a significant decrease in percent freezing in Tg negative/CCI mice vs. Tg negative/sham. SynCav1/CCI mice (open bars) demonstrated significant preserved or improved Hpc-dependent learning and memory *P = 0.03 compared with Tg negative/CCI mice. C) No significant difference between groups was observed in cued reexposure on d 3. Data (n = 21–22 mice/group) are presented as means ± sem. P < 0.05.