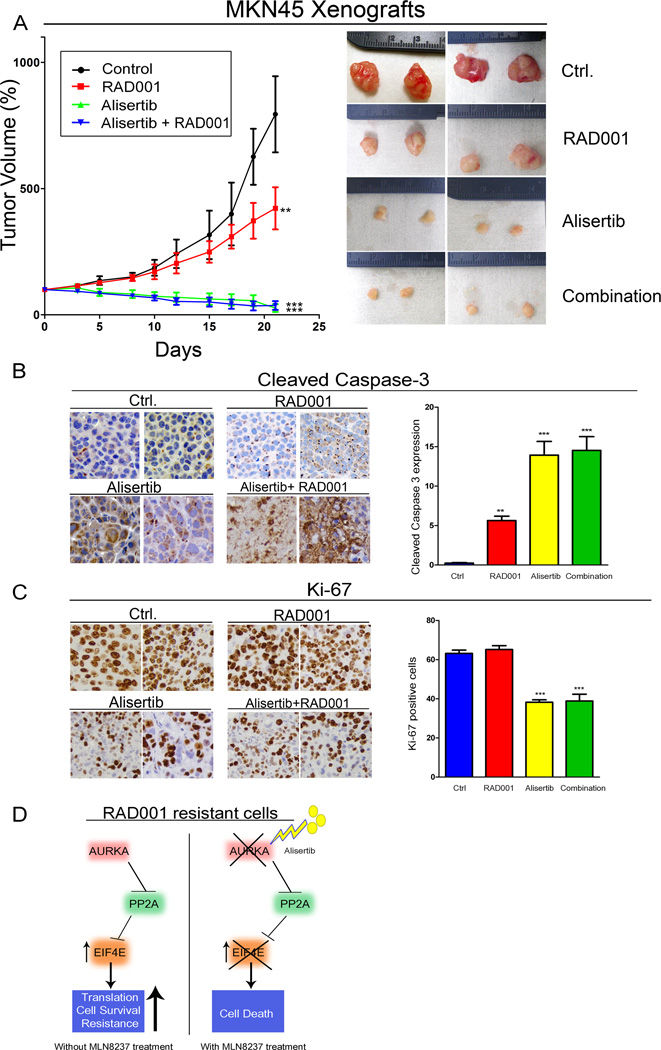
Figure 6. Alisertib treatment reduces tumor growth in intrinsic RAD001 resistant xenograft mouse model.
A) Animals injected with MKN45 cells, and the tumors were allowed to grow until 200 mm3 in size, then treated with RAD001, alisertib or their combination for 5 weeks. Data indicated that alisertib alone or in combination with RAD001 significantly reduced tumor size in comparison with untreated or RAD001 alone treated groups. Although tumors in RAD001 treatment alone grew at a significantly slower rate than those in untreated group, they continued to grow, confirming the intrinsic resistant phenotype to RAD001. B and C) Immunohistochemistry analysis for cleaved caspase-3 expression, marker of apoptosis, and Ki-67 expression, marker of proliferation, in representative tumors of treated groups. D) A schematic diagram showing a proposed mechanism of RAD001 resistance. AURKA expression promotes RAD001 resistance through inhibition of PP2A, which leads to activation of EIF4E. Inhibition of AURKA by alisertib restores PP2A activity, thereby inhibiting EIF4E and inducing death in RAD001 resistant cancer cells.