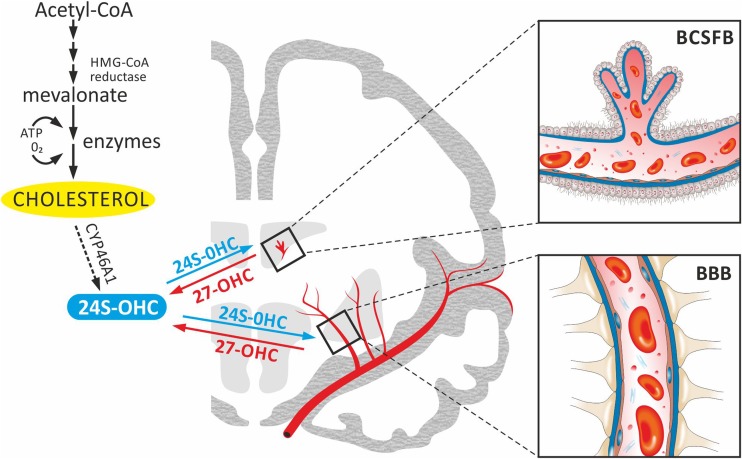
Fig. 1.
Cholesterol synthesis and metabolism in the brain. Brain cholesterol is synthesized from acetyl-CoA to mevalonate by HMG-CoA reductase. Subsequently, it is converted to cholesterol in numerous enzymatic reactions, dependent on access to ATP and O2. Excess cholesterol is converted to the 24S-OHC and removed from the brain because its accumulation is highly toxic to neurons and may induce their apoptosis. A part of the cholesterol pool is taken up from the general pool as the 27-OHC by diffusion. This is possible because of the oxysterols’ ability of crossing the functional barrier systems: BBB (formed by cerebrovascular endothelial cells) and BCSFB (formed by epithelial cells of the choroid plexus). Abbreviations: 24S–OHC 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol, 27-OHC 27-hydroxycholesterol, acetyl-CoA acetyl coenzyme A, BBB the blood brain barrier, BCSFB the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier, HMG-CoA reductase 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase