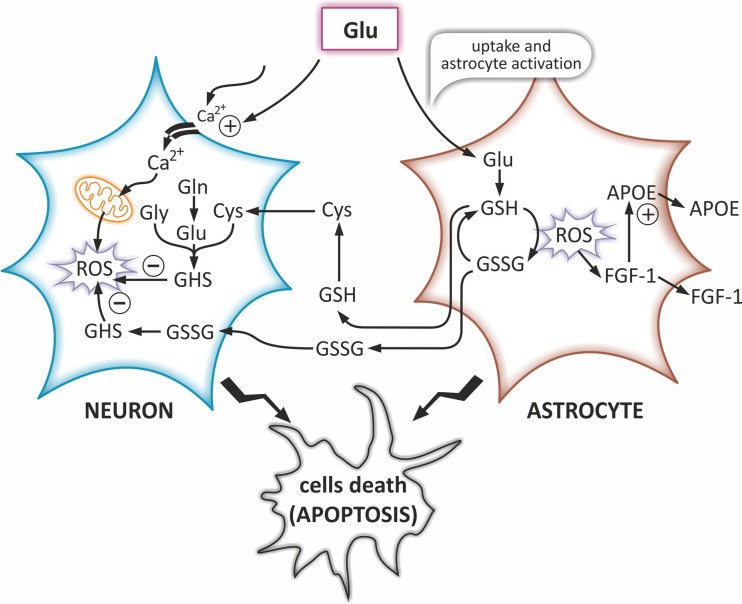
Fig. 3.
Impact of oxidative stress on cholesterol homeostasis in astrocytes and neurons. Glutamatergic neurotransmission is associated with the influx of Ca2+ ions inside the neuron that in turn induces the ROS production in the mitochondria. This can lead to neuronal damage and consequently triggers antioxidant systems that increase the production and secretion of the GSH. Astrocytes uptake Glu and thus remove it from the synaptic cleft in order to protect neurons from the excitotoxic effect. Moreover, Glu is one of the substrates for GSH synthesis in astrocytes. Under the oxidative stress conditions, there are also produced ROS in astrocytes, which contribute to GSH oxidation into GSSG. Both the GSH and the GSSG are released into the extracellular space and converted by the ectoenzymes to precursors of GSH synthesis in neurons. In the presence of ROS, FGF-1 enhances the synthesis of APOE and both the FGF-1 and the APOE are released from astrocytes. Prolonged exposure of astrocytes and neurons to oxidative stress leads to initiation of cell death processes. Abbreviations: APOE apolipoprotein E, Glu glutamate, GSH glutathione, GSSG glutathione disulfide, FGF-1 a fibroblast growth factor 1, ROS reactive oxygen species