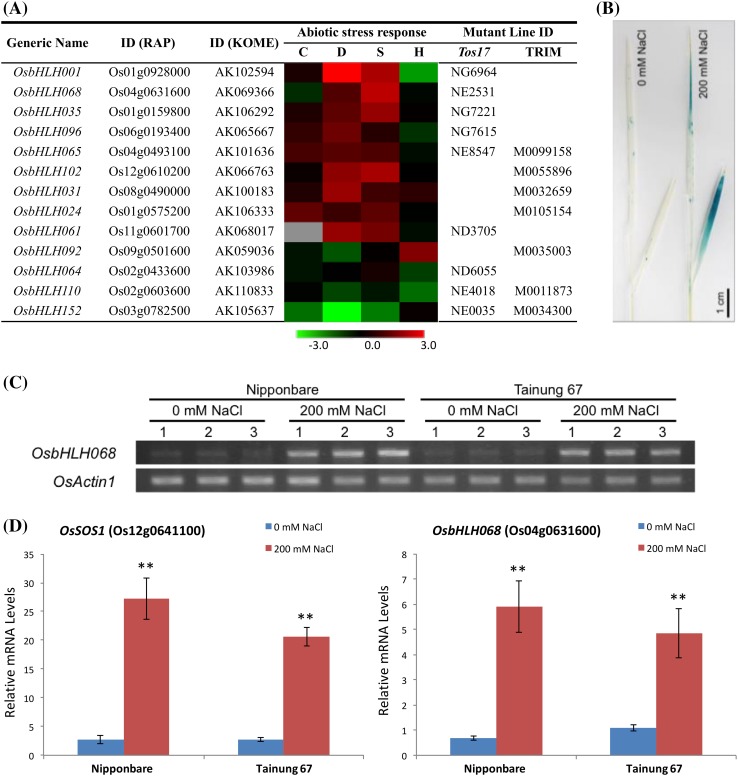
Fig. 1.
Salt-enhanced OsbHLH068 expression. a Abiotic stress-responsive OsbHLHs. Red and green indicate increased and decreased gene expression, respectively. The scale bar shows log2-fold changes. C, cold treatment; D, drought treatment; H, heat treatment; S, salt treatment. Tos17, rice Tos17 insertion mutant database; TRIM, Taiwan rice insert mutant database. b Histochemical staining of the aerial tissues in OsbHLH068p::GUS transgenic Tainung 67 (Oryza sativa L. spp. japonica cv. Tainung 67) seedlings. c The expression pattern of OsbHLH068 in Nipponbare (Oryza sativa L. spp. japonica cv. Nipponbare) and Tainung 67 aerial tissues by RT-PCR. The Arabic numerals represent the individual rice plants. d Quantification of OsSOS1 and OsbHLH068 mRNA levels in Nipponbare and Tainung 67 aerial tissues by qPCR. The values are the mean ± SD of two independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test. Seedlings used for GUS staining (b), RT-PCR (c), and qPCR (d) assays were grown on basal medium for 13 days and then transferred to basal medium containing 0 or 200 mM NaCl for an additional day