FIGURE 1.
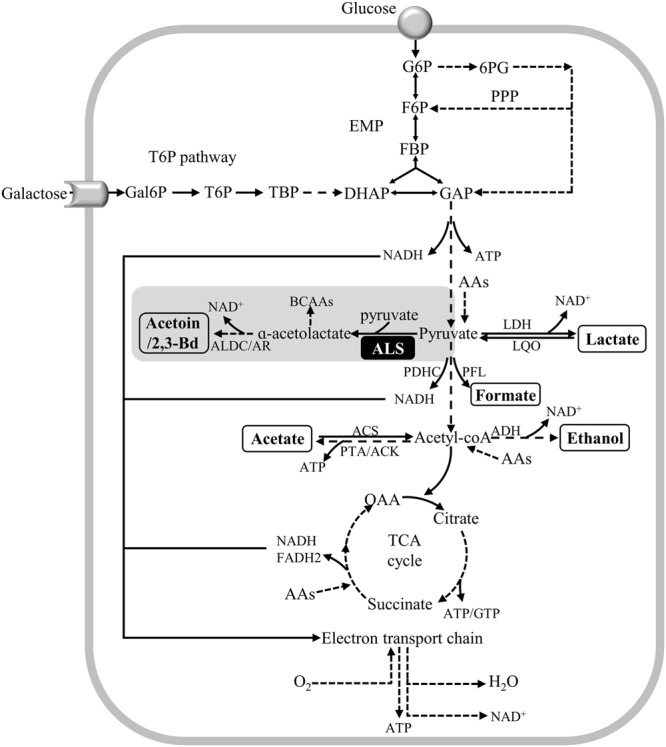
Schematic representation of metabolic pathways of Staphylococcus aureus glucose and galactose catabolism. Galactose is catabolized in the tagatose 6-phosphate pathway into the glycolytic intermediates DHAP and GAP. DHAP and GAP originated from galactose and glucose are oxidized to pyruvate in the EMP (glycolysis) pathway, which can be reduced to lactate, α-acetolactate and/or acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA can be converted to acetate, to generate ATP, and ethanol. Alternatively, acetyl-CoA can be used to produce citrate for the citric acid cycle (TCA cycle). Under aerobic conditions, the NADH molecules formed in the EMP and TCA cycle are oxidized in the respiratory chain, thereby restoring the redox balance, and producing ATP. Proposed pathways were reconstructed based on genome information (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genomes/lproks.cgi), literature and database surveys (KEGG, MetaCyc). Inside boxes are the end products of pyruvate metabolism. Inside the black box is the ALS enzyme. AAs, amino acids; ACS, acetyl-CoA synthetase; ADH, bifunctional acetaldehyde-CoA/alcohol dehydrogenase; ALDC/AR, α-acetolactate decarboxylase/acetoin reductase; ALS, α-acetolactate synthase; BCAAs, branched-chain amino acids; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; FBP, fructose 1,6-bisphosphate; F6P, fructose 6-phosphate; Gal6P, galactose 6-phosphate; GAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate; G6P, glucose 6-phosphate; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; LQO, lactate-quinone oxidoreductase; PDHC, pyruvate dehydrogenase complex; PFL, pyruvate formate-lyase; 6-PG, 6-phosphogluconate; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; PTA/ACK, phosphotransacetylase/acetate kinase; OAA, oxaloacetate; TBP, tagatose 1,6-bisphosphate; T6P, tagatose 6-phosphate.
