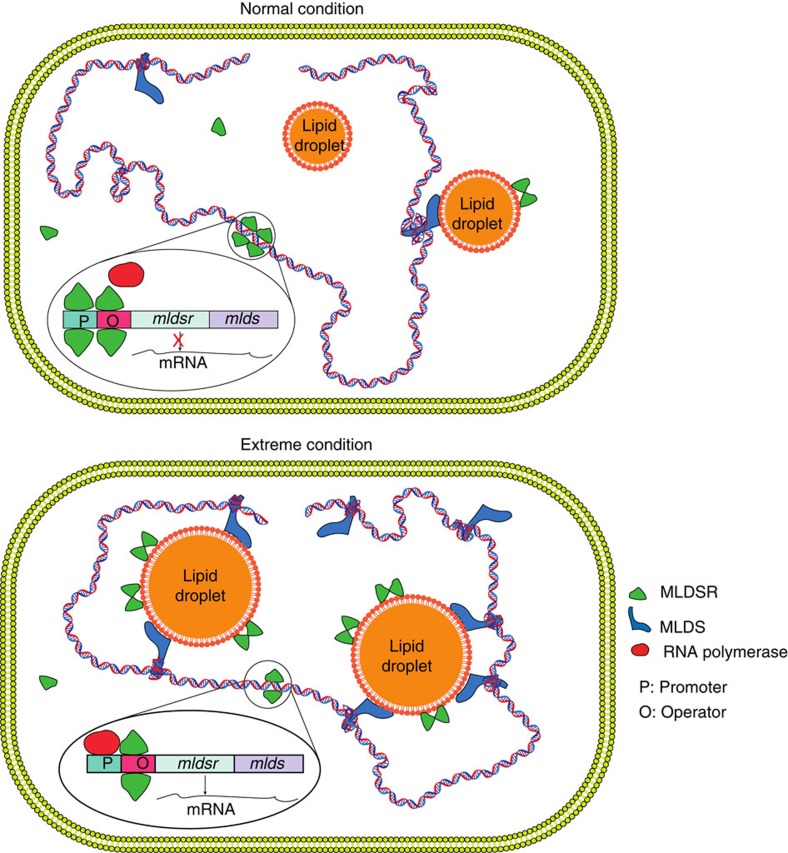
Figure 8. Proposed functions for LDs as well as MLDS and MLDSR during acclimation to stressful conditions.
Under normal conditions, MLDSR in the cytosol represses expression of both MLDSR and MLDS, which might be due to inhibition of RNA polymerase binding to the promoter. Since MLDS is a major protein that binds DNA to LDs, decreasing MLDS on LDs reduces binding of genomic DNA to the organelle. In contrast, under stressful conditions, more MLDSR molecules are translocated to LDs, reducing the cytosolic concentration, which in turn enhances the expression of MLDS and MLDSR. The increased MLDS on LDs drives the binding of genomic DNA to LDs, which exerts a protective effect, such as reducing DNA damage.