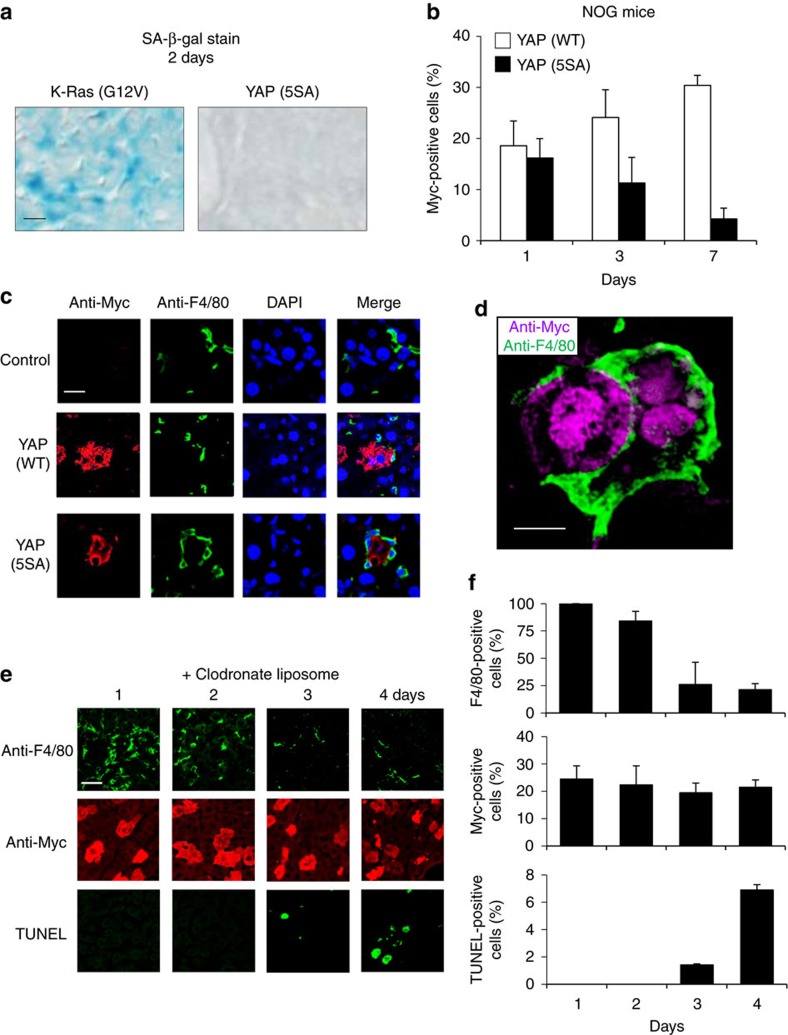
Figure 2. YAP activation leads to hepatocyte apoptosis and engulfment by Kupffer cells in mouse liver.
(a) Light microscopy to detect SA-β-gal-stained cells in liver sections of mice expressing the indicated molecules on day 2 post-HTVi. Scale bar, 10 μm (n=3). (b) Quantification of percentages of Myc+ cells in confocal immunofluorescence images of NOG mice expressing Myc-tagged YAP (WT) or YAP (5SA) assayed on the indicated days post-HTVi. Data are the mean±s.d. (n=3). (c) Representative confocal immunofluorescence images of the liver sections stained with anti-Myc, anti-F4/80 or 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) on day 3 post-HTVi. Control, without HTVi. Scale bar, 20 μm (n=3). (d) High magnification image of the liver sections stained with anti-Myc or anti-F4/80 on day 3 post-HTVi (× 60 objective lens). Scale bar, 10 μm (n=3). (e) Representative confocal immunofluorescence images of livers expressing Myc-tagged YAP (5SA) and treated with clodronate liposomes for the indicated days post-HTVi to deplete Kupffer cells. Sections were stained with anti-Myc, anti-F4/80 or TUNEL as indicated. Scale bar, 10 μm (n=4). (f) Quantification of percentages of cells positive for F4/80, Myc or TUNEL in the liver sections in (e). Data are the mean±s.d. (n=4).