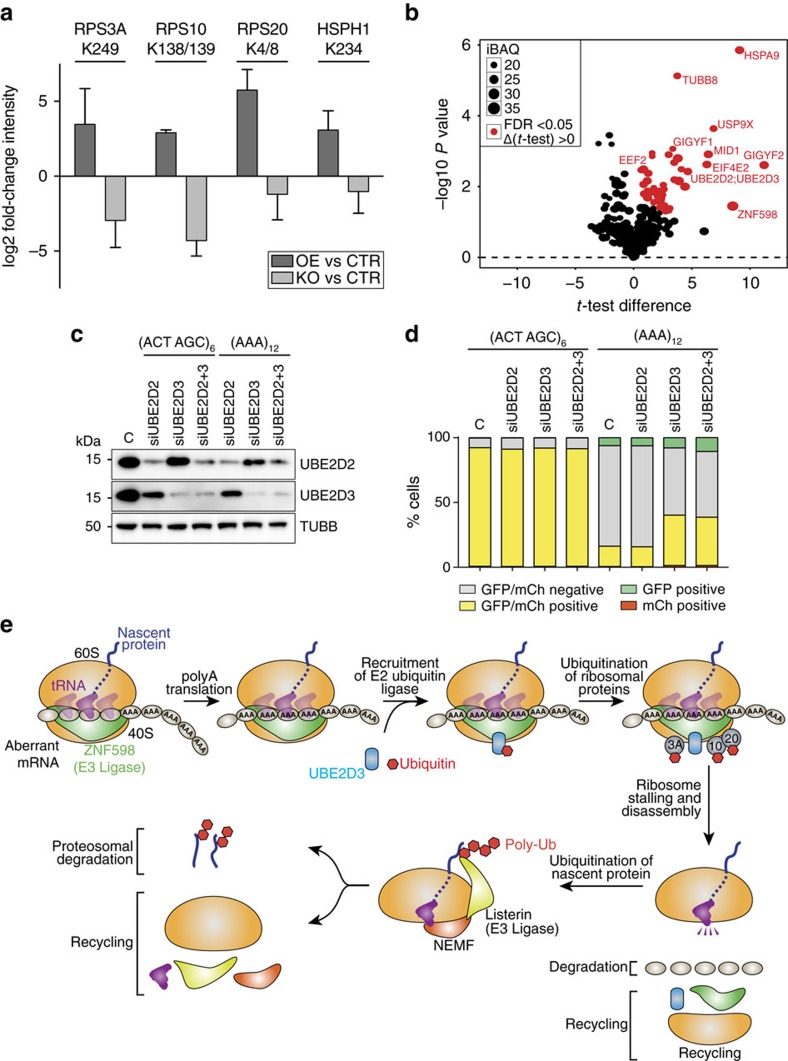
Figure 4. Ribosome stalling at coding polyA sequences requires the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity of ZNF598 and the E2 ubiquitin ligase UBE2D3.
(a) Identification of differentially ubiquitinated proteins by ubiquitin remnant immuno-affinity profiling. Log2 ratios of the enrichment of the quantified diGly-containing peptides are shown. Only peptides with an average log2 ≥2 upregulation for ZNF598OE/CTR and downregulation for ZNF598KO/CTR are shown. Error bars represent the s.d. (n=2). See Supplementary Data 5 for a complete list of all detected peptides. (b) Volcano plots of the quantitative proteomic analysis of the ZNF598 interactome. The t-test difference based on label free quantitation for each detected protein is plotted against the negative logarithmic P value of a Welch’s t-test. The intensity based absolute quantitation (iBAQ)51 values correspond to the sum of all the peptide intensities divided by the number of observable peptides of a protein and are represented by point size. Proteins with a permutation-based FDR-value of <5% and t-test difference >0 are labelled in red and represent putative ZNF598 interactors (see also Supplementary Fig. 15 and Supplementary Data 6). (c) Analysis of siRNA-mediated knockdown of UBE2D2, UBE2D3 or both UBE2D2 and UBE2D3 in HEK293 cells by western blot. C indicates mock transfection. (d) Detection of GFP and mCherry fluorescent signals by FACS analyses in samples from (c), for reporter constructs containing (ACT AGC)6 and (AAA)12 linkers. Each experiment was performed in triplicate. (e) Model for ZNF598-dependent ribosome stalling and RQC at cryptic polyadenylated protein-coding mRNAs.