Fig. 2.
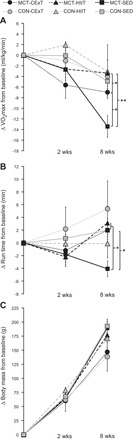
Aerobic exercise capacity and body mass. A: for rats with MCT (40 mg/kg)-induced PAH (black symbols), decrement in V̇o2max (expressed relative to body mass) was ameliorated by both a HIIT approach (gray triangles, n = 8) and a CExT (gray circles, n = 7) vs. untrained MCT (SED, black squares, n = 10), with change after 6 wk of training (8-wk time point) compared with pretraining (2-wk time point) not different (P > 0.05) from that in healthy HIIT, CExT, and SED control rats (CON, gray symbols, n = 5–6 ea). B: MCT-induced decrement in treadmill run time (time to V̇o2max) was also significantly improved by CExT and HIIT. C: body mass was significantly impacted by time for all groups but not differently affected by group assignment. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
