Fig. 7.
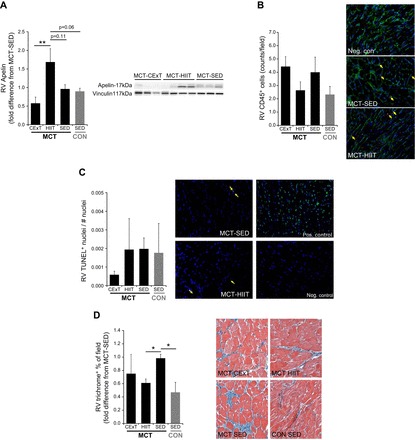
RV inflammation, apoptosis, fibrosis, and apelin expression. A: immunoblotting of RV homogenates for the anti-apoptotic/anti-inflammatory mediator and positive inotropic regulator apelin in rats with MCT-induced (40 mg/kg) PAH (MCT, black bars) and untreated healthy CON rats (gray bars) revealed a higher protein abundance in MCT that were trained with HIIT (n = 8) but not with CExT (n = 7). Values are expressed as fold difference from untrained (SED) MCT (n = 8). In fixed RV sections of MCT rats (black bars) and untreated healthy CON rats (gray bars), infiltration of CD45+ cells (lymphocytes, B) measured by immunofluorescent staining (count/field, mean ± SE) was not different from untrained animals (SED), either after a HIIT or CExT approach. Adjacent panels are representative images, with arrows indicating examples of CD45+ (red) cells, green representing wheat-germ agglutin-stained myocyte membrane, and blue representing nuclei. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL) staining for myocyte apoptosis was also performed (% of TUNEL+ cells, mean ± SE, C). Adjacent panels are representative images, including a positive and negative control slide, with arrows indicating examples of TUNEL+ (bright green) cells and blue representing nonapoptotic nuclei. RV sections were additionally assessed for fibrosis with Masson’s trichrome (blue, in images) staining (D), and MCT-induced increase in RV fibrosis (expressed as fold difference from MCT-SED in %positively stained field) was less for HIIT-trained MCT. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01.
